{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Module 4.2. Compile the pretrained PyTorch model from model zoo with SageMaker Neo\n",
"---\n",
"\n",
"***[Before getting started] This notebook loads and compiles pre-trained models from model-zoo right away, so you can run them standalone. If you want to fine-tune or use the model-zoo instead of your own model, this notebook is convenient and useful.***\n",
"\n",
"In this notebook, we compile and deploy a pre-trained model on the ImageNet dataset with SageMaker Neo. SageMaker Neo is an API that optimizes machine learning models for hardware, and models compiled with Neo can run anywhere in the cloud and on edge devices.\n",
"\n",
"As of Nov. 2021, SageMaker Neo supports PyTorch 1.8.0 on cloud instances and edge devices, and PyTorch 1.5.1 on AWS Inferentia.\n",
"\n",
"Please refer to the link below for instance types, hardware, and deep learning frameworks supported by SageMaker Neo.\n",
"\n",
"- Cloud Instance: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/neo-supported-cloud.html\n",
"- Edge Device: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/neo-supported-devices-edge.html\n",
"\n",
"This hands-on can be completed in about **10 minutes**. "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"%load_ext autoreload\n",
"%autoreload 2\n",
"%store -r\n",
"%store"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import logging, sys\n",
"def _get_logger():\n",
" '''\n",
" # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17745914/python-logging-module-is-printing-lines-multiple-times\n",
" '''\n",
" loglevel = logging.DEBUG\n",
" l = logging.getLogger(__name__)\n",
" if not l.hasHandlers():\n",
" l.setLevel(loglevel)\n",
" logging.getLogger().addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)) \n",
" l.handler_set = True\n",
" return l \n",
"\n",
"logger = _get_logger()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import os, sys, sagemaker\n",
"sys.path.insert(0, \"./src\")\n",
"#!{sys.executable} -m pip install -qU \"sagemaker>=2.45\"\n",
"print(sagemaker.__version__)\n",
"model_trace_name = 'model.pth'\n",
"sample_img_path = \"sample_images\""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
\n",
"\n",
"# 1. Inference script\n",
"---\n",
"\n",
"The code cell below stores the SageMaker inference script in the `src` directory."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"%%writefile src/infer_pytorch_neo.py\n",
"\n",
"import io\n",
"import json\n",
"import logging\n",
"import os\n",
"import pickle\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"import torch\n",
"import torchvision.transforms as transforms\n",
"from PIL import Image # Training container doesn't have this package\n",
"\n",
"logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)\n",
"logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"def model_fn(model_dir):\n",
" import neopytorch\n",
"\n",
" logger.info(\"model_fn\")\n",
" neopytorch.config(model_dir=model_dir, neo_runtime=True)\n",
" device = torch.device(\"cuda\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\n",
" # The compiled model is saved as \"compiled.pt\"\n",
" model = torch.jit.load(os.path.join(model_dir, \"compiled.pt\"), map_location=device)\n",
"\n",
" # It is recommended to run warm-up inference during model load\n",
" sample_input_path = os.path.join(model_dir, \"sample_input.pkl\")\n",
" with open(sample_input_path, \"rb\") as input_file:\n",
" model_input = pickle.load(input_file)\n",
" if torch.is_tensor(model_input):\n",
" model_input = model_input.to(device)\n",
" model(model_input)\n",
" elif isinstance(model_input, tuple):\n",
" model_input = (inp.to(device) for inp in model_input if torch.is_tensor(inp))\n",
" model(*model_input)\n",
" else:\n",
" print(\"Only supports a torch tensor or a tuple of torch tensors\")\n",
"\n",
" return model\n",
" \n",
" \n",
"def transform_fn(model, payload, request_content_type='application/octet-stream', \n",
" response_content_type='application/json'):\n",
"\n",
" logger.info('Invoking user-defined transform function')\n",
"\n",
" if request_content_type != 'application/octet-stream':\n",
" raise RuntimeError(\n",
" 'Content type must be application/octet-stream. Provided: {0}'.format(request_content_type))\n",
"\n",
" # preprocess\n",
" decoded = Image.open(io.BytesIO(payload))\n",
" preprocess = transforms.Compose([\n",
" transforms.Resize(256),\n",
" transforms.CenterCrop(224),\n",
" transforms.ToTensor(),\n",
" transforms.Normalize(\n",
" mean=[\n",
" 0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[\n",
" 0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),\n",
" ])\n",
" normalized = preprocess(decoded)\n",
" batchified = normalized.unsqueeze(0)\n",
"\n",
" # predict\n",
" device = torch.device(\"cuda\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\n",
" batchified = batchified.to(device)\n",
" result = model.forward(batchified)\n",
"\n",
" # Softmax (assumes batch size 1)\n",
" result = np.squeeze(result.detach().cpu().numpy())\n",
" result_exp = np.exp(result - np.max(result))\n",
" result = result_exp / np.sum(result_exp)\n",
"\n",
" response_body = json.dumps(result.tolist())\n",
"\n",
" return response_body, response_content_type"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
\n",
"\n",
"# 2. Load trained model\n",
"---\n",
"\n",
"Load the trained model. In order to reduce compatibility issues with different framework versions and issues during serialization, it is recommended to initialize the model structure first and load the model weights rather than loading the entire model as much as possible."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import torch\n",
"import torchvision.models as models\n",
"import tarfile\n",
"import src.train_utils as train_utils\n",
"\n",
"classes_dict = train_utils.load_classes_dict('classes_dict_imagenet.json')\n",
"num_classes = len(classes_dict)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Detect if we have a GPU available\n",
"device = torch.device(\"cuda:0\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\n",
"model = models.mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True)\n",
"model = model.to(device)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import torch\n",
"import torchvision.models as models\n",
"import tarfile\n",
"\n",
"input_shape = [1,3,224,224]\n",
"dummy_input = torch.zeros(input_shape).float()\n",
"dummy_input = dummy_input.to(device)\n",
"trace = torch.jit.trace(model.float().eval(), dummy_input)\n",
"trace.save(model_trace_name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Local Inference without Endpoint\n",
"\n",
"Debugging while performing inference in a local environment is recommended because there are many risks to directly deploying a trained model to a production environment without sufficient testing. Please refer to the code in the code cell below as an example."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Once the model deployment is complete, let's do some inference."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import os\n",
"import json\n",
"import random\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"from io import BytesIO\n",
"from PIL import Image\n",
"import src.infer_utils as infer_utils\n",
"from src.infer_pytorch_neo import transform_fn\n",
"\n",
"model = torch.jit.load(model_trace_name)\n",
"model = model.to(device)\n",
"\n",
"img_list = os.listdir(sample_img_path)\n",
"img_path_list = [os.path.join(sample_img_path, img) for img in img_list]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"test_idx = random.randint(0, len(img_list)-1)\n",
"img_path = img_path_list[0]\n",
"\n",
"with open(img_path, mode='rb') as file:\n",
" payload = bytearray(file.read())\n",
" \n",
"response_body, _ = transform_fn(model, payload)\n",
"result = json.loads(response_body)\n",
"infer_utils.parse_result(result, classes_dict, img_path, show_img=True)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
\n",
"\n",
"# 3. Compile Model with SageMaker Neo\n",
"---\n",
"\n",
"## Overview\n",
"\n",
"Neo-AI supports various frameworks and automatically optimizes models with minimal loss of accuracy. The Neo-AI compiler automatically optimizes the model for the target device's OS and hardware platform, and transforms the model into an executable form in a deep learning runtime. Deep Learning Runtime can perform inference with just two lines of code regardless of deep learning frameworks and edge devices, and the version is constantly updated.\n",
"\n",
"And, if you have an AWS account, you can use Amazon SageMaker Neo powered by Neo-AI. SageMaker Neo compiles models suitable for multiple target devices at the same time with one click on a few lines of code or UI, without any additional package or infrastructure setup, and without charging.\n",
"\n",
"## (Deep Dive) SageMaker Neo Stack\n",
"\n",
"Let's take a closer look at the SageMaker Neo Stack. Neo first optimizes the model with the compiler, and then runs the compiled model through the runtime in the cloud or on-device.\n",
"\n",
"For compiler part, the computational graph generator loads deep learning models trained on various deep learning platforms and reconstructs them into graph structures. It then converts the operators defined in the model into primiative operators to create a computational graph.\n",
"After the graph is created, an optimized graph is created by applying various graph optimization techniques.\n",
"\n",
"However, hardware-dependent optimization considering the target hardware architecture on which the model will operate is not possible with only an optimized graph.\n",
"Therefore, it is necessary to transform the computational graph into IR(Intermediate Representation), which is a form of hardware-dependent optimization.\n",
"\n",
"Relay IR generates code after performing hardware-dependent optimizations such as memory allocation, parallelization, and execution order based on the generated IR. For more details, please check the paper.\n",
"\n",
"It should be noted here that Apache TVM is not always used. Depending on the deep learning framework or hardware specifications, TensorRT or TreeLite is used. For NVIDIA GPUs, Neo uses TensorRT.\n",
"\n",
"Finally, the backend code generator generates backend code optimized for the target hardware architecture (CPU, GPU, TPU, etc.) where the deep learning model workload will be deployed based on IR.\n",
"\n",
"The runtime part is done through the DLR. It's only a few megabytes, not hundreds of megabytes like TensorFlow or PyTorch.\n",
"\n",
"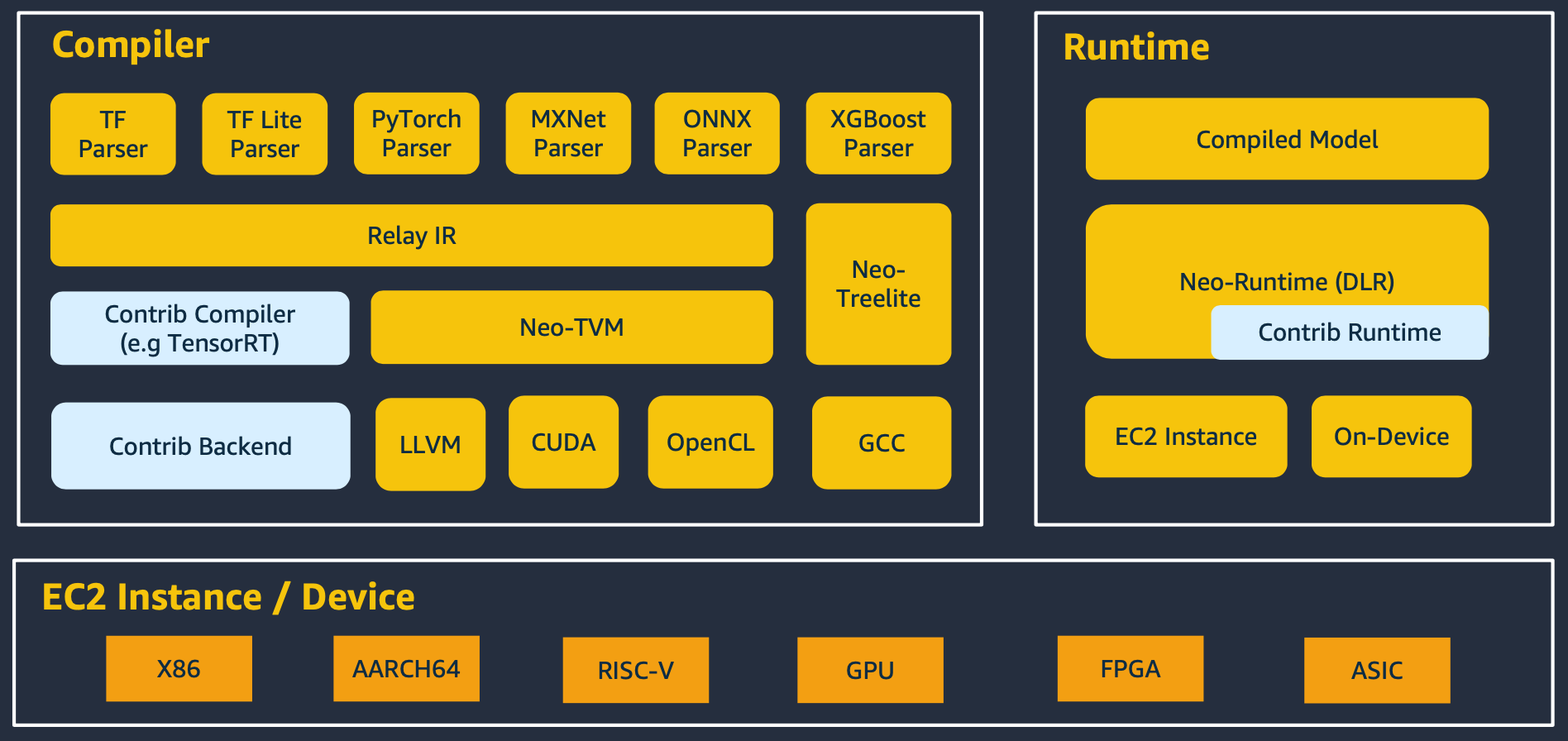\n",
"\n",
"- Relay IR: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.00952.pdf \n",
"\n",
"\n",
"## (Deep Dive) Graph Optimization\n",
"\n",
"Most model compilers perform graph optimizations as shown in the diagram.\n",
"Graph optimization reduces the number of layers and computational complexity with techniques such as operator fusion, tensor fusion, and layer fusion.\n",
"\n",
"Let's take an example of calculating 1/sqrt(w) as an example of operator fusion. The graph before optimization requires a total of 2 operations with w > sqrt > div, but if $1/\\sqrt{w}$ is stored as a pre-computation value, no operation is required.\n",
"\n",
"In the figure, three operations conv, bias, and Relu are bundled into one CBR (Conv, Bias, Relu) block to process consecutive operations in one function. This is called vertical layer fusion.\n",
"Also, there are 3 overlapping 1x1 CBR blocks, which can be reduced to one block. This is called horizontal layer fusion.\n",
"\n",
"According to NVIDIA's experiments, the total number of layers used in the ResNet-152 network was 670, but reduced to 159 through graph optimization.\n",
"\n",
"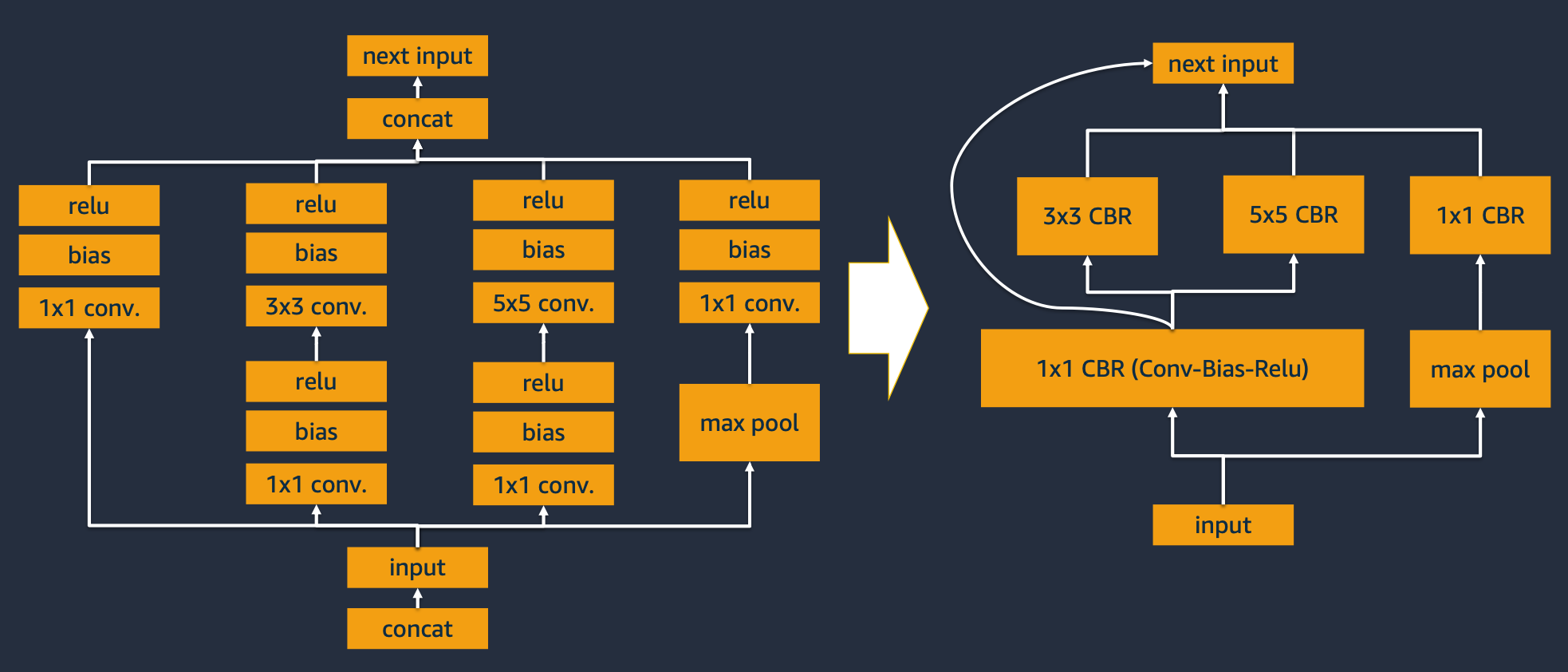\n",
"\n",
"- TensorRT Overview: https://blogs.nvidia.co.kr/2020/02/19/nvidia-tensor-rt/ \n",
"\n",
"\n",
"## Model Compression"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"with tarfile.open('model.tar.gz', 'w:gz') as f:\n",
" f.add(model_trace_name)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Model Compilation\n",
"\n",
"The code below compiles the model for 4 use cases.\n",
"- Cloud (CPU, `ml_m5` instance)\n",
"- Cloud (CPU, `ml_c5` instance)\n",
"- Cloud (GPU, `ml_g4dn` instance)\n",
"- NVIDIA Jetson nano (CPU)\n",
"- NVIDIA Jetson nano (GPU)\n",
"\n",
"Depending on NVIDIA Jetpack, the CUDA version or TensorRT version of the device may not be compatible, and it takes tens of seconds to load the GPU model, so it is a good strategy to compile and test the CPU model together.\n",
"\n",
"Compilation takes usually 4-6 minutes.\n",
"\n",
"**[Caution] If you get an error while compiling, please be sure to check the PyTorch version of the notebook running this code. The PyTorch version must match. This hands-on uses PyTorch 1.6.**"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import time, boto3, sagemaker\n",
"role = sagemaker.get_execution_role()\n",
"bucket = sagemaker.Session().default_bucket()\n",
"\n",
"# For cloud ML inference\n",
"compilation_job_cloud_cpu_m4 = infer_utils.compile_model_for_cloud(\n",
" role, bucket, target_device='ml_m4', dataset_dir=dataset_dir\n",
")\n",
"compilation_job_cloud_cpu_c5 = infer_utils.compile_model_for_cloud(\n",
" role, bucket, target_device='ml_c5', dataset_dir=dataset_dir\n",
")\n",
"compilation_job_cloud_gpu = infer_utils.compile_model_for_cloud(\n",
" role, bucket, target_device='ml_g4dn', dataset_dir=dataset_dir\n",
")\n",
"\n",
"# For on-device ML inference\n",
"compilation_job_jetson_cpu = infer_utils.compile_model_for_jetson(\n",
" role, bucket, dataset_dir=dataset_dir, use_gpu=False\n",
")\n",
"compilation_job_jetson_gpu = infer_utils.compile_model_for_jetson(\n",
" role, bucket, dataset_dir=dataset_dir, use_gpu=True\n",
")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"compilation_jobs = [compilation_job_cloud_cpu_m4, compilation_job_cloud_cpu_c5, compilation_job_cloud_gpu, \n",
" compilation_job_jetson_cpu, compilation_job_jetson_gpu]"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"compilation_job_cloud_cpu_m4['response']['CompilationJobArn']"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"sm_client = boto3.client('sagemaker')\n",
"\n",
"max_time = time.time() + 15*60 # 15 mins\n",
"for job in compilation_jobs:\n",
" while time.time() < max_time:\n",
" resp = sm_client.describe_compilation_job(CompilationJobName=job['job_name']) \n",
" if resp['CompilationJobStatus'] in ['STARTING', 'INPROGRESS']:\n",
" print('Running...')\n",
" else:\n",
" print(resp['CompilationJobStatus'], job)\n",
" break\n",
" time.sleep(30)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Review Compilation Jobs on AWS Console"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from IPython.core.display import display, HTML\n",
"region = boto3.Session().region_name\n",
"\n",
"for job in compilation_jobs:\n",
" job_name = job['job_name']\n",
" display(\n",
" HTML(\n",
" 'Review Compilation Job for {}'.format(\n",
" region, job_name, job_name\n",
" )\n",
" )\n",
" )"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Copy Compiled model to local\n",
"This code cell copies the compiled model from S3 to local. In the case of the cloud, real-time deployment can be performed by creating the endpoint of the instance, and in the case of on-device like NVIDIA Jetson nano, copy the model to the device and install DLR. With DLR, you can easily infer models with simple API calls without the need to install a separate framework such as PyTorch and TensorFlow.\n",
"\n",
"- Installing DLR: https://neo-ai-dlr.readthedocs.io/en/latest/install.html"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"model_root_path = 'neo-model'\n",
"!rm -rf {model_root_path}\n",
"for job in compilation_jobs:\n",
" model_path = f\"{model_root_path}/{job['job_name']}\"\n",
" os.makedirs(model_path, exist_ok=True)\n",
" !aws s3 cp {job['s3_compiled_model_path']} {model_path} --recursive "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Wrap-up"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"If you continue to do hands-on deploying Greengrass ML component in the Cloud9 environment, take note of the output of the code cell below. You must run the shell command below on Cloud9.\n",
"\n",
"```shell\n",
"rm -rf model_cpu\n",
"mkdir model_cpu && cd model_cpu\n",
"aws s3 cp [MODEL-CLOUD-CPU-S3-PATH] . --recursive\n",
"tar -xzvf model-ml_m4.tar.gz && rm model-ml_m4.tar.gz\n",
"```"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"model_cloud_cpu_s3_path = compilation_jobs[0]['s3_compiled_model_path']\n",
"print(model_cloud_cpu_s3_path)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### (Optional) Clean-up"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# !rm -rf model neo-custom-model output model.pth model.tar.gz {dataset_dir}"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "conda_pytorch_p37",
"language": "python",
"name": "conda_pytorch_p37"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.7.10"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}