# Using SageMaker with Aurora
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. This lab will walk you through the process of integrating Aurora with SageMaker Endpoints to infer customer churn in a data set using SQL commands.
This lab contains the following tasks:
1. Create an IAM role to allow Aurora to interface with SageMaker
2. Associate the IAM role with the Aurora DB cluster
3. Add the IAM role to the DB cluster parameter group and apply it
4. Create a SageMaker integration function in Aurora
5. Run SageMaker inferences from Aurora
This lab requires the following prerequisites:
* [Get Started](/prereqs/environment/) (choose **Yes** for the **Enable Aurora ML Labs?** feature option)
* [Connect to the Cloud9 Desktop](/prereqs/connect/)
* [Create a New DB Cluster](/provisioned/create/) (conditional, only if you plan to create a cluster manually)
* [Overview and Prerequisites](/ml/overview/)
## 1. Create an IAM role to allow Aurora to interface with SageMaker
If you have not already opened a terminal window in the Cloud9 desktop in a previous lab, please [following these instructions](/prereqs/connect/) to do so now. Once connected, run the command below which will create an IAM role, and access policy.
```
aws iam create-role --role-name auroralab-sagemaker-access \
--assume-role-policy-document "{\"Version\":\"2012-10-17\",\"Statement\":[{\"Effect\":\"Allow\",\"Principal\":{\"Service\":\"rds.amazonaws.com\"},\"Action\":\"sts:AssumeRole\"}]}"
sed -i "s%EndpointArn%$(aws sagemaker describe-endpoint --endpoint-name auroraml-churn-endpoint --query [EndpointArn] --output text)%" sagemaker_policy.json
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name auroralab-sagemaker-access --policy-name inline-policy \
--policy-document file://sagemaker_policy.json
```
## 2. Associate the IAM role with the Aurora DB cluster
Associate the role with the DB cluster by using following command:
```
aws rds add-role-to-db-cluster --db-cluster-identifier auroralab-mysql-cluster \
--role-arn $(aws iam list-roles --query 'Roles[?RoleName==`auroralab-sagemaker-access`].Arn' --output text)
```
Next, run the following command and repeat until the output shows as **available**, before moving on to the next step.
```
aws rds describe-db-clusters --db-cluster-identifier auroralab-mysql-cluster \
--query 'DBClusters[*].[Status]' --output text
```
## 3. Add the IAM role to the DB cluster parameter group and apply it
Set the ==aws_default_sagemaker_role== cluster-level parameter to the ARN of the IAM role we created in the first step of this lab. Run the following command:
```
aws rds modify-db-cluster-parameter-group \
--db-cluster-parameter-group-name $DBCLUSTERPG \
--parameters "ParameterName=aws_default_sagemaker_role,ParameterValue=$(aws iam list-roles --query 'Roles[?RoleName==`auroralab-sagemaker-access`].Arn' --output text),ApplyMethod=pending-reboot"
```
Reboot the DB cluster for the change to take effect. To minimize downtime use the manual failover process to trigger the reboot:
```
aws rds failover-db-cluster --db-cluster-identifier auroralab-mysql-cluster
```
Run the following command and wait until the output shows as **available**, before moving on to the next step:
```
aws rds describe-db-clusters --db-cluster-identifier auroralab-mysql-cluster \
--query 'DBClusters[*].[Status]' --output text
```
## 4. Create a SageMaker integration function in Aurora
Run the command below, replacing the ==[clusterEndpoint]== placeholder with the cluster endpoint of your DB cluster to connect to the database:
```
mysql -h[clusterEndpoint] -u$DBUSER -p"$DBPASS" mltest
```
Once connected, execute the following SQL query to create the **will_churn** function in the database, using the ==alias aws_sagemaker_invoke_endpoint== parameter and passing the name of the SageMaker endpoint.
??? tip "What is a SageMaker Endpoint?"
To simplify the Aurora labs, a SageMaker model has been trained and deployed automatically for you. These resources were deployed when you selected **Yes** for the **Enable Aurora ML Labs?** feature option when you deployed the labs environment using CloudFormation.
Amazon SageMaker also provides model hosting services for model deployment. Amazon SageMaker provides an HTTPS endpoint where your machine learning model is available to provide inferences.
```
CREATE FUNCTION `will_churn`(
state varchar(2048),
acc_length bigint(20),
area_code bigint(20),
int_plan varchar(2048),
vmail_plan varchar(2048),
vmail_msg bigint(20),
day_mins double,
day_calls bigint(20),
eve_mins double,
eve_calls bigint(20),
night_mins double,
night_calls bigint(20),
int_mins double,
int_calls bigint(20),
cust_service_calls bigint(20)
) RETURNS varchar(2048) CHARSET latin1
alias aws_sagemaker_invoke_endpoint
endpoint name 'auroraml-churn-endpoint';
```
## 5. Run SageMaker inferences from Aurora
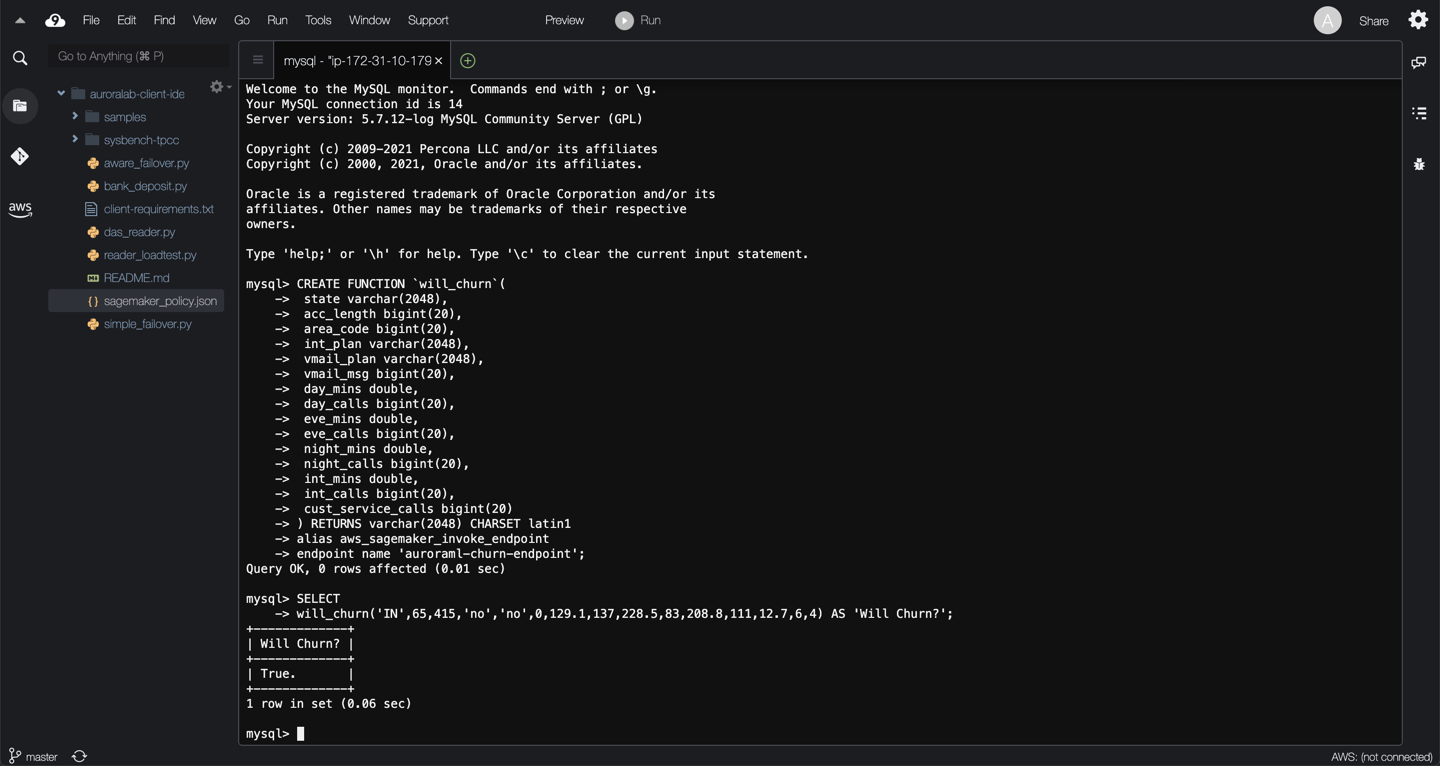
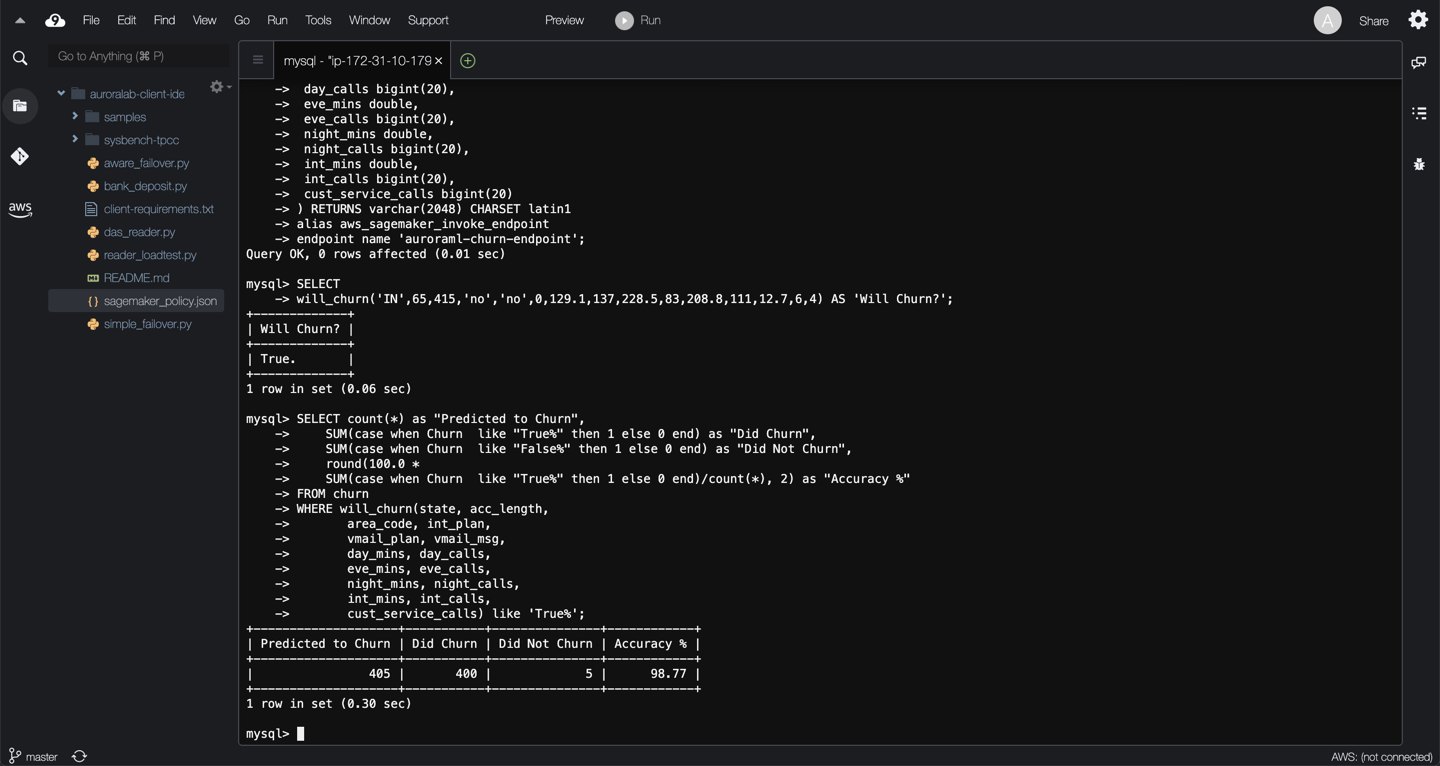
Now that we have an integration function linking back to the SageMaker endpoint, the DB cluster can pass values to SageMaker and retrieve inferences. In this example, we will submit values from the `churn` table as function inputs to determine if a particular customer **will churn**. This is represented by the **"True"** result in the **‘Will Churn?’** column as shown in the screenshot.
```
SELECT
will_churn('IN',65,415,'no','no',0,129.1,137,228.5,83,208.8,111,12.7,6,4) AS 'Will Churn?';
```
To continue the example, we will compare the training data with the SageMaker model's outputs. The `churn` table already contains the actual churn outcomes for particular customers. We will compare these results with the inferred results using the function to understand the model's effectiveness, by executing following query:
```
SELECT count(*) as "Predicted to Churn",
SUM(case when Churn like "True%" then 1 else 0 end) as "Did Churn",
SUM(case when Churn like "False%" then 1 else 0 end) as "Did Not Churn",
round(100.0 *
SUM(case when Churn like "True%" then 1 else 0 end)/count(*), 2) as "Accuracy %"
FROM churn
WHERE will_churn(state, acc_length,
area_code, int_plan,
vmail_plan, vmail_msg,
day_mins, day_calls,
eve_mins, eve_calls,
night_mins, night_calls,
int_mins, int_calls,
cust_service_calls) like 'True%';
```
Based on the query result, this SageMaker model is 99.25% accurate.
Disconnect from the DB cluster, using:
```
quit;
```