# Create an Aurora Serverless DB Cluster
This lab will walk you through the steps of creating an Amazon Aurora Serverless database cluster manually, and configuring the scaling parameters of the cluster.
This lab contains the following tasks:
1. Create a serverless DB cluster
2. Create a secret to store the credentials
This lab requires the following lab modules to be completed first:
* [Get Started](/prereqs/environment/) (you do not need to provision a DB cluster automatically)
## 1. Create a serverless DB cluster
Open the Amazon RDS service console, if you don't already have it open.
Click **Create database** to start the configuration process
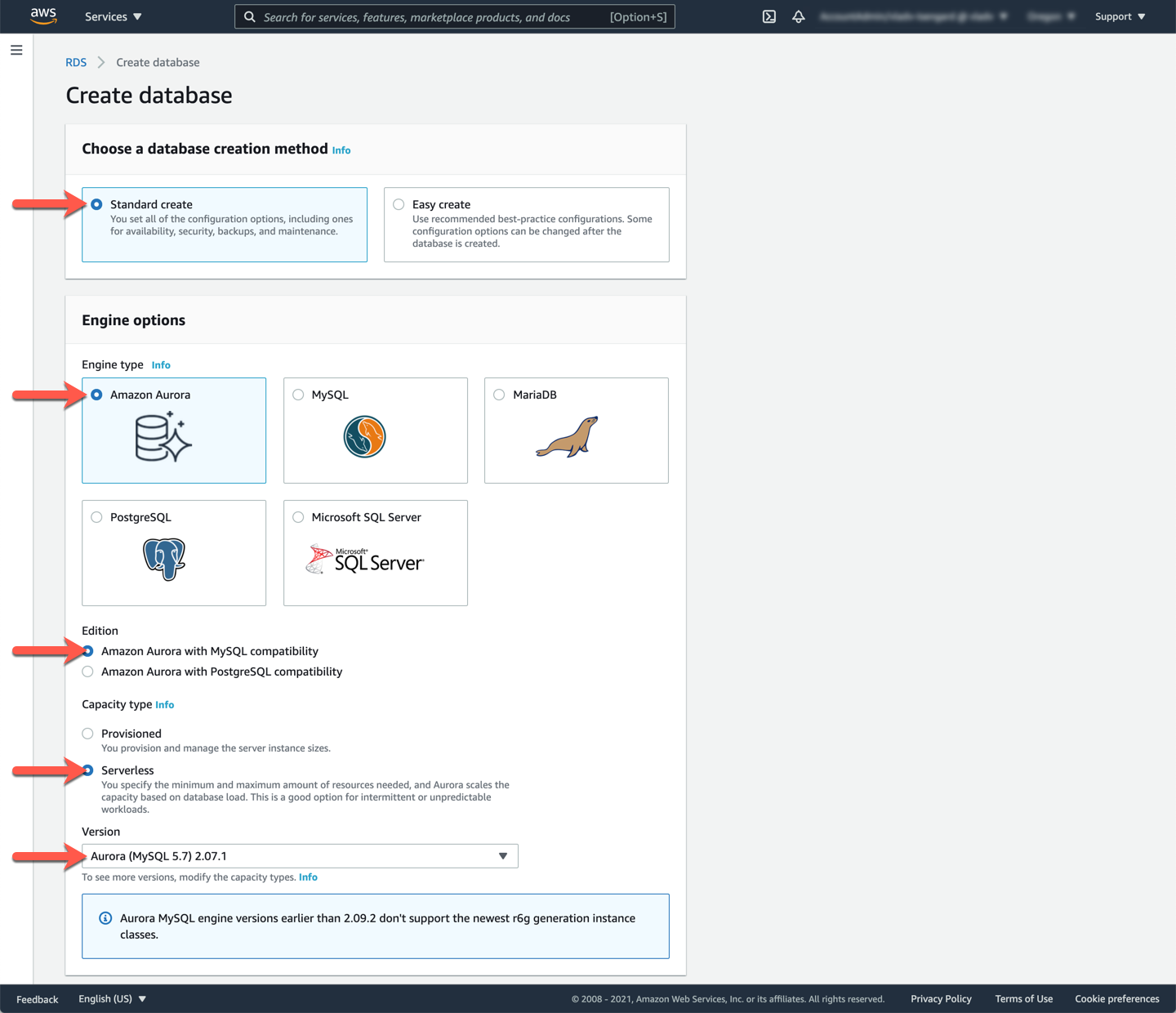
In the first configuration section of the **Create database** page, ensure the **Standard Create** database creation method is selected.
Next, in the **Engine options** section, choose the **Amazon Aurora** engine type, the **Amazon Aurora with MySQL compatibility** edition, the **Serverless** capacity type, and the latest **Aurora (MySQL 5.7) X.XX.X** version.
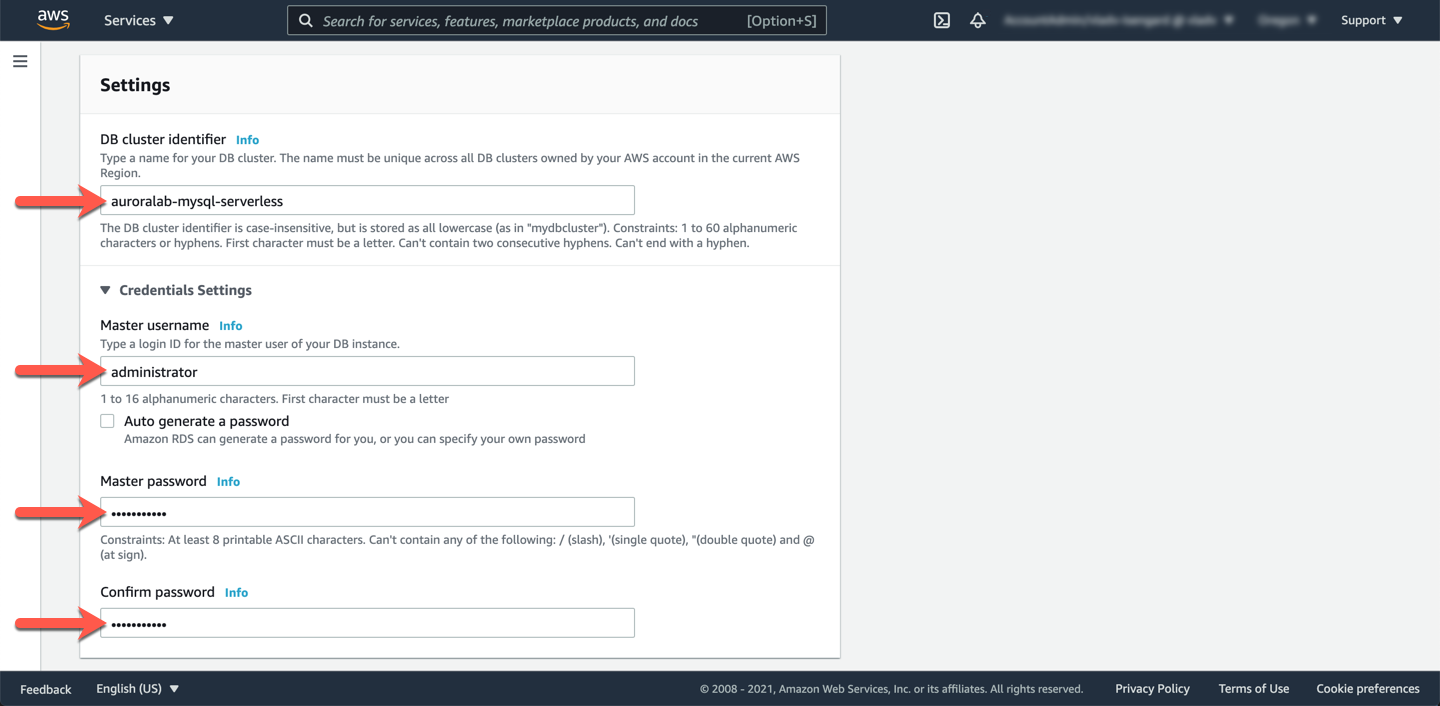
In the **Settings** section set the database cluster identifier to `auroralab-mysql-serverless`. Configure the name and password of the master database user, with the most elevated permissions in the database. We recommend to use the user name `administrator` for consistency with subsequent labs and a password of your choosing. For simplicity ensure the check box **Auto generate a password** is **not checked**.
In the **Capacity settings** section, choose a **Minimum Aurora capacity unit** of `1 (2GB RAM)` and a **Maximum Aurora capacity unit** of `8 (16 GB RAM)`. Next, expand the **Additional scaling configuration** section, and **check** the box next to **Pause compute capacity after consecutive minutes of inactivity**. This configuration will allow Aurora Serverless to scale the capacity of your DB cluster between 1 capacity unit and 16 capacity units, and to suspend capacity entirely after 5 minutes of inactivity.
In the **Connectivity** section, expand the sub-section called **Additional configuration**. This section allows you to specify where the database cluster will be deployed within your defined network configuration. Your environment has been deployed with a VPC that includes all resources needed for an Aurora database cluster. This includes the VPC itself, subnets, DB subnet groups, security groups and several other networking constructs. All you need to do is select the appropriate existing connectivity controls in this section.
Pick the **Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)** named `auroralab-vpc`. The lab environment also configured a **VPC security group** that allows your lab workspace EC2 instance to connect to the database. Make sure the **Choose existing** security group option is selected and from the dropdown pick the security group named `auroralab-database-sg`. Please remove any other security groups, such as `default` from the selection.
Additionally, please check the box **Data API**, to enable integration with the RDS Data API.
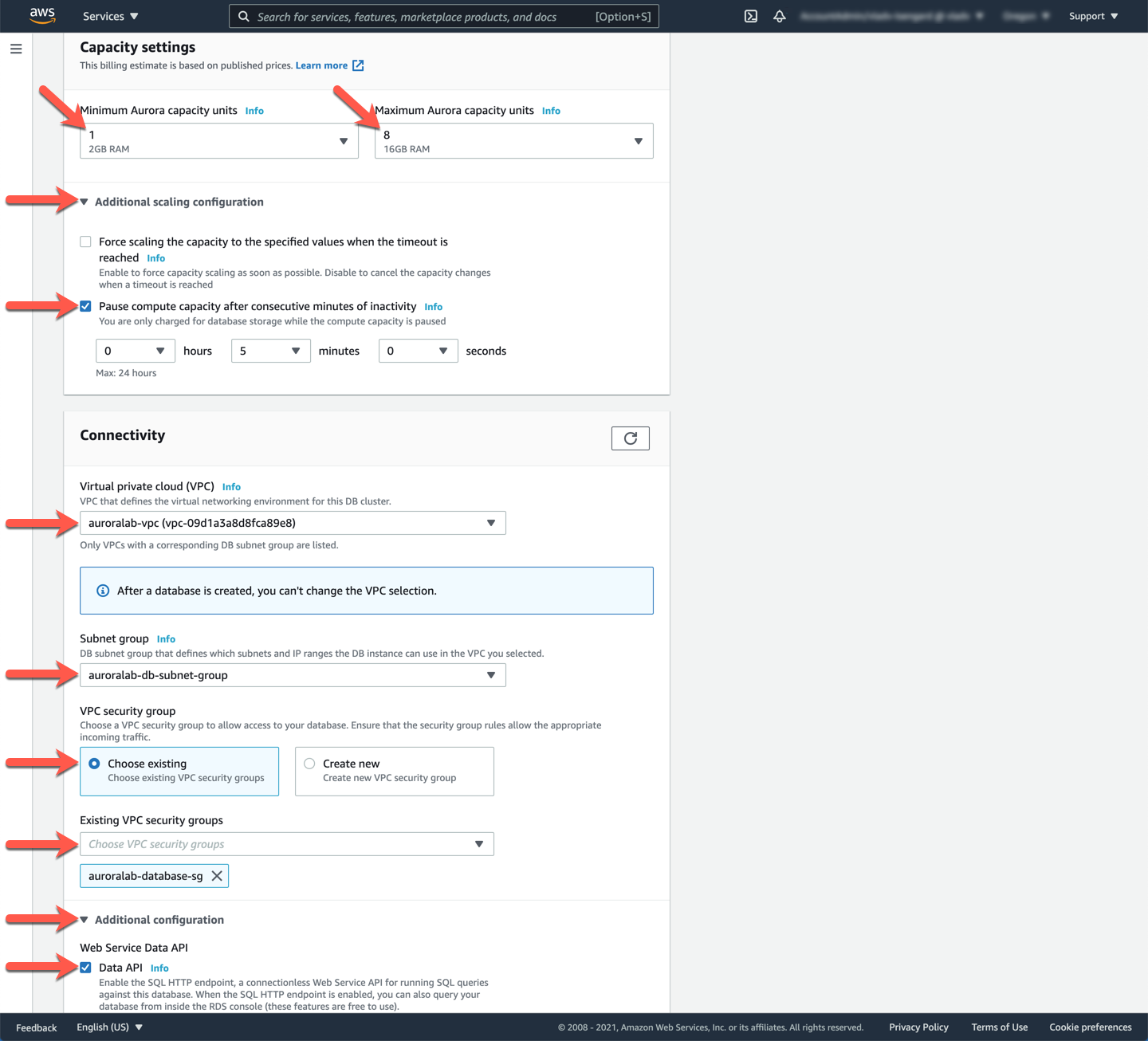
Next, expand the **Additional configuration** section. Type `mylab` in the **Initial database name** text box. Choose a `1 day` **Backup retention period**. **De-select** the check box **Enable delete protection**. In a production use case, you will want to leave that option checked, but for testing purposes, un-checking this option will make it easier to clean up the resources once you have completed the labs.
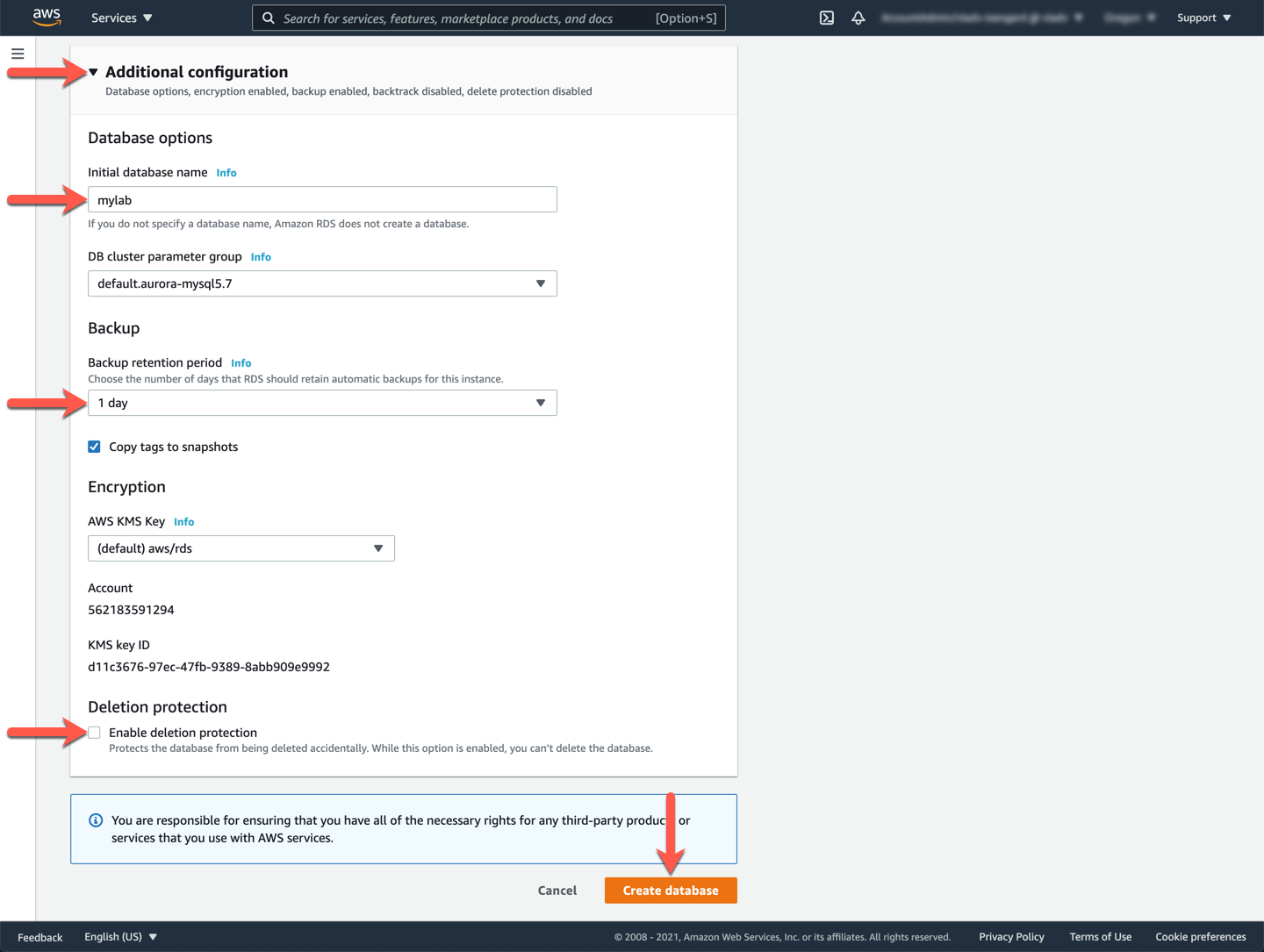
??? tip "What do these selections mean?"
You will create a database cluster with the following characteristics:
* Aurora MySQL 5.7 compatible (latest engine version)
* Serverless db cluster scaling between 1 and 16 capacity units, and pausing compute capacity after 5 minutes of inactivity
* Deployed in the VPC and using the network configuration of the lab environment
* Integrated with the RDS Data API
* Automatically backed up continuously, retaining backups for 1 day
* Using data at rest encryption
Click **Create database** to provision the DB cluster.
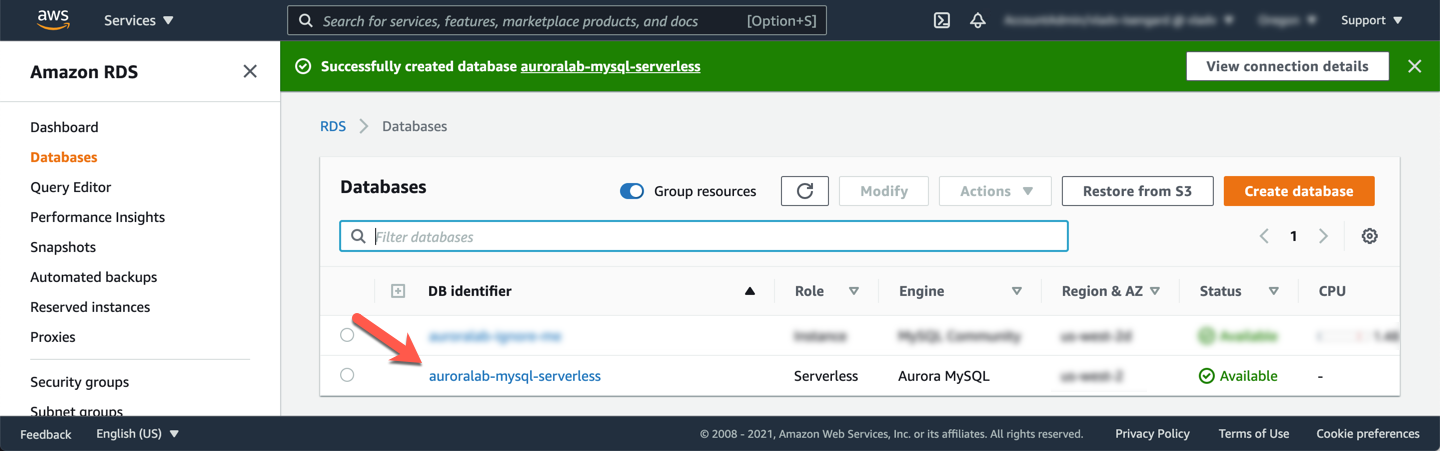
Once back to the list of databases, click the name of the new database in the listing.
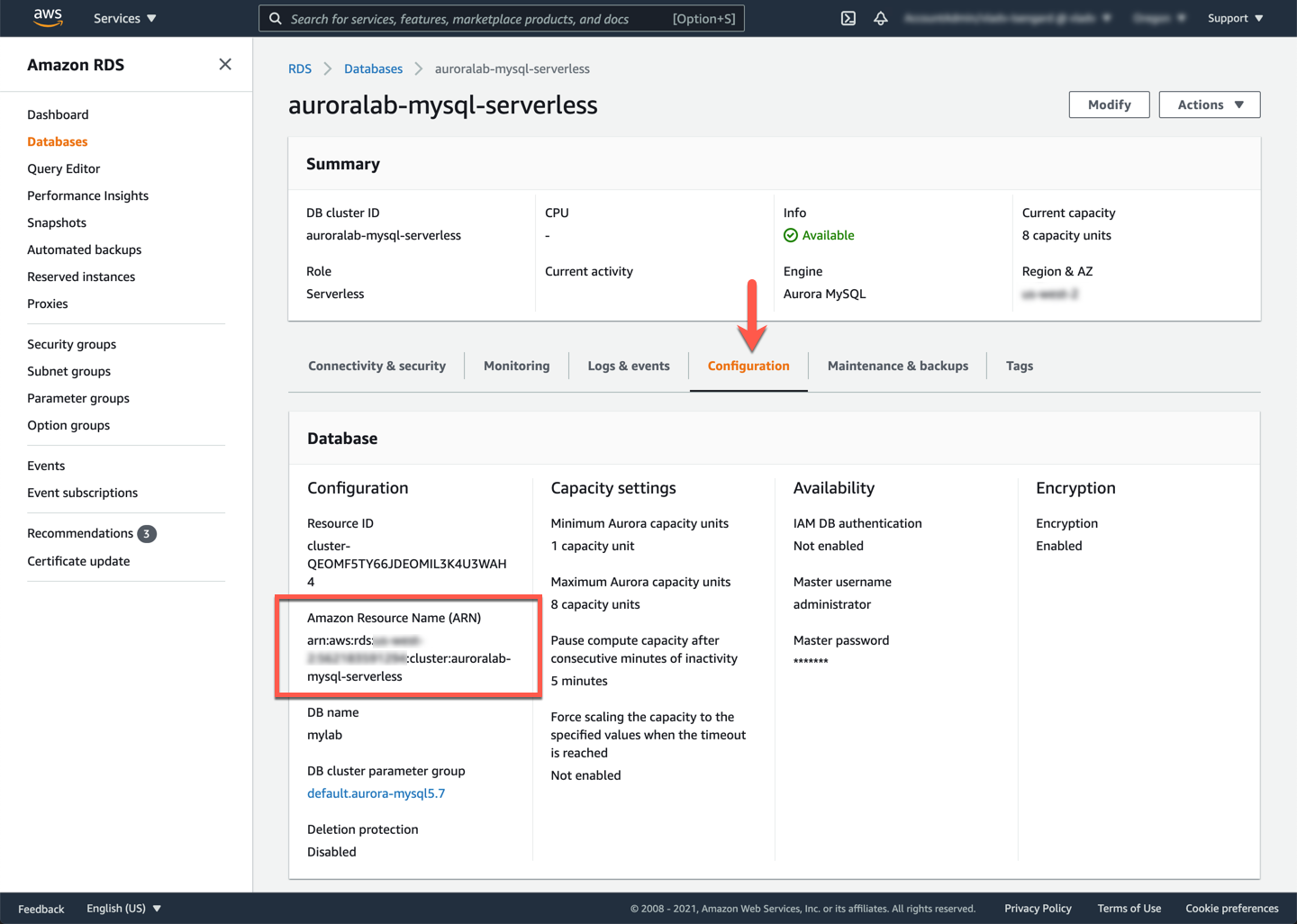
In the details view of the cluster, click on the **Configuration** tab. Note the value for **ARN**. Write this down, you will need it later.
## 2. Create a secret to store the credentials
Open the AWS Secrets Manager service console.
Click **Store a new secret** to start the configuration process.
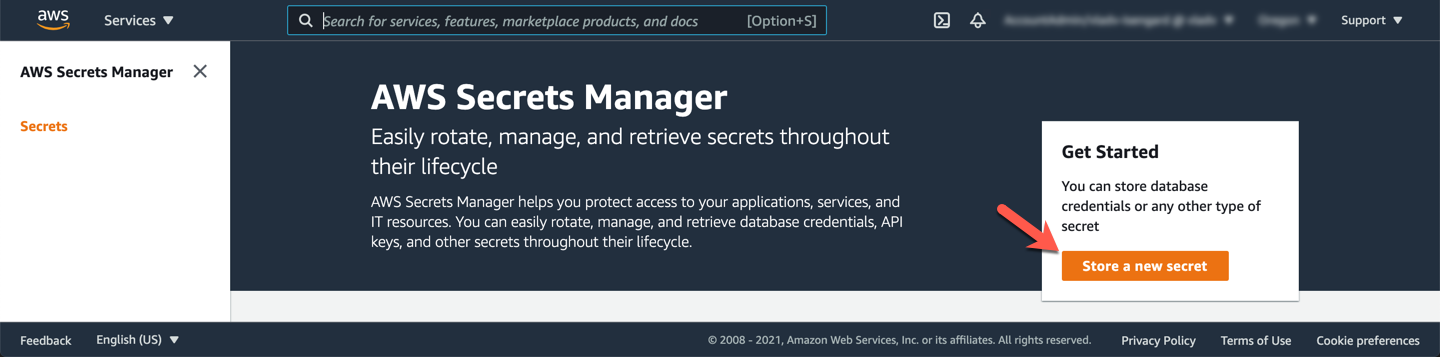
In the **Select secret type** section, choose **Credentials for RDS database**, then input the **User name** (e.g. `administrator`) and **Password** that you provided when you created the serverless DB cluster.
Next, in the **Select which RDS database this secret will access** section, choose the DB cluster identifier you assigned to your cluster (e.g. `auroralab-mysql-serverless`). Click **Next**.
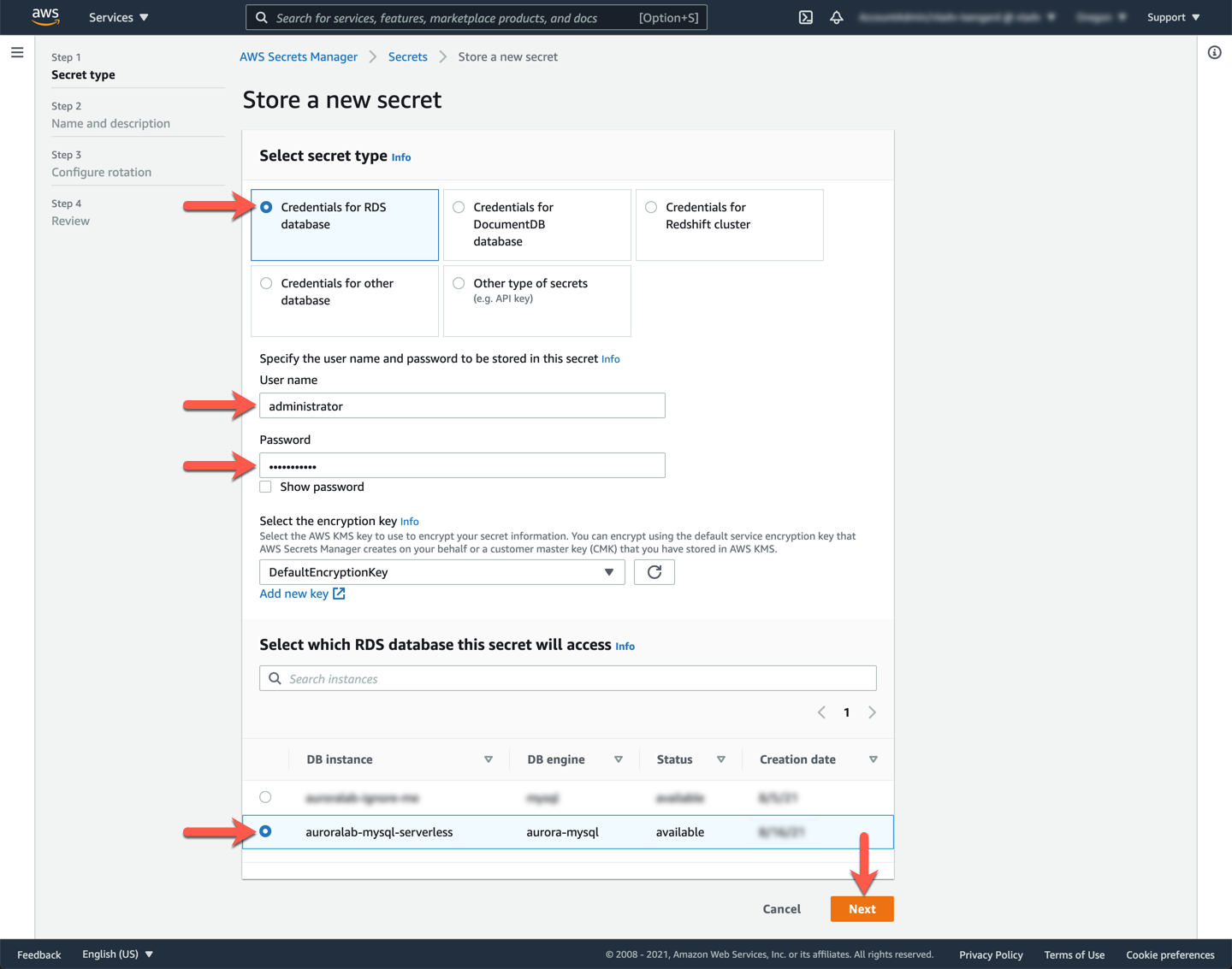
Name the secret `auroralab-mysql-serverless-secret` and provide a relevant description for the secret, then click **Next**.
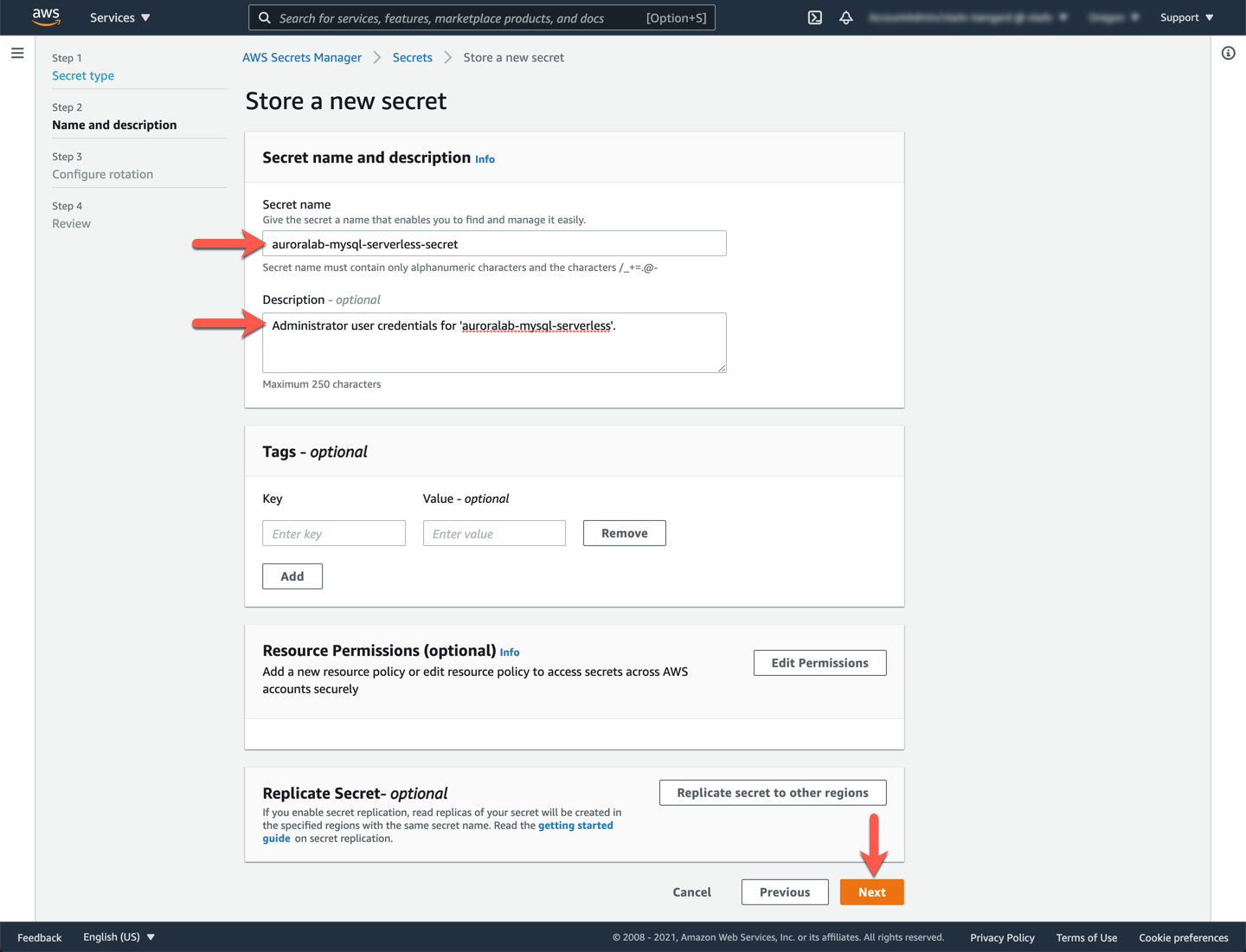
Finally, in the **Configure automatic rotation** section, leave the option of **Disable automatic rotation** selected. In a production environment you will want to use database credentials that rotate automatically for additional security. Click **Next**.
In the **Review** section you have the ability to check the configuration parameters for your secret, before it gets created. Additionally, you can retrieve sample code in popular programming languages, so you can easily retrieve secrets into your application. Click **Store** at the bottom of the screen.
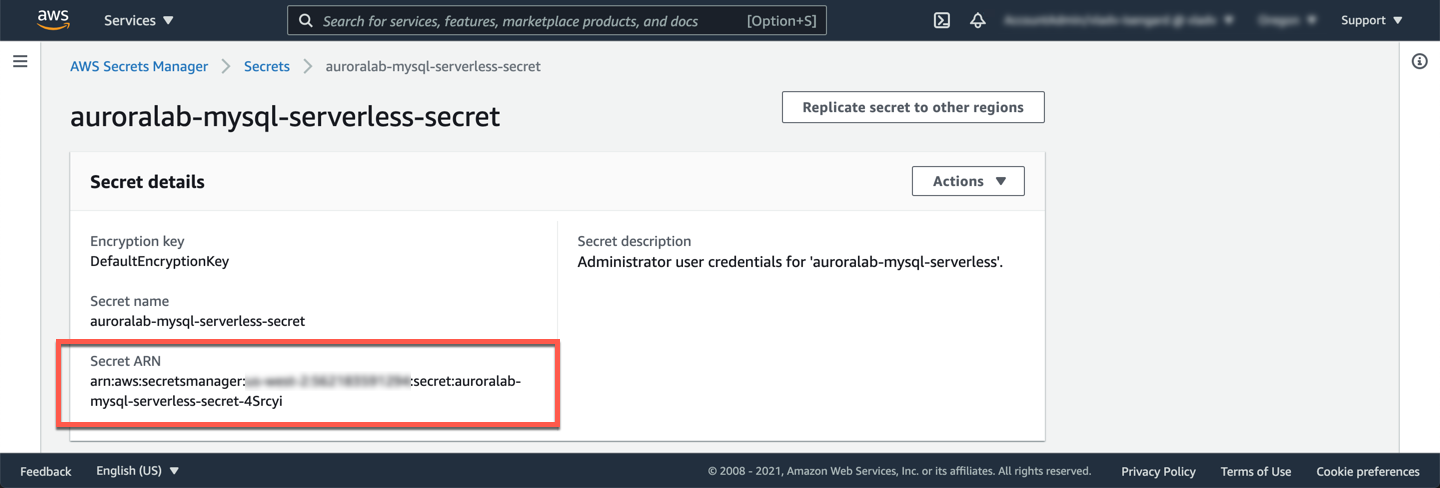
Once created, identify the **ARN** of the newly created secret. This value will be needed in subsequent labs. In the list of **Secrets** in the console, click on the name of the newly created secret.
In the detail view of the secret, note the value for **Secret ARN**. Write this down, you will need it later.