# Use Aurora Serverless with AWS Lambda Functions
This lab will show you how to connect to and interact with Amazon Aurora Serverless database clusters using AWS Lambda functions and the RDS Data API.
This lab contains the following tasks:
1. Create a Lambda execution role
2. Create a Lambda function
3. Connect to the database using the RDS Data API
This lab requires the following lab modules to be completed first:
* [Get Started](/prereqs/environment/) (you do not need to provision a DB cluster automatically)
* [Create an Aurora Serverless DB Cluster](/serverless/create/)
## 1. Create a Lambda execution role
Before you create an AWS Lambda function, you need to configure an IAM execution role. This will contain the permissions you are granting the function to interact with AWS resources via the APIs. Open the Identity and Access Management (IAM) service console. Choose **Roles** from the left hand side menu, if it isn't already selected, and click **Create role**.
!!! warning "Console Experience Updates"
The IAM service team is in the process of updating the service console web interface to improve the experience. The console views you see when you go through the labs may differ than the examples below. Once the chnages are finalized, we will update the examples below to reflect the changes where appropriate.
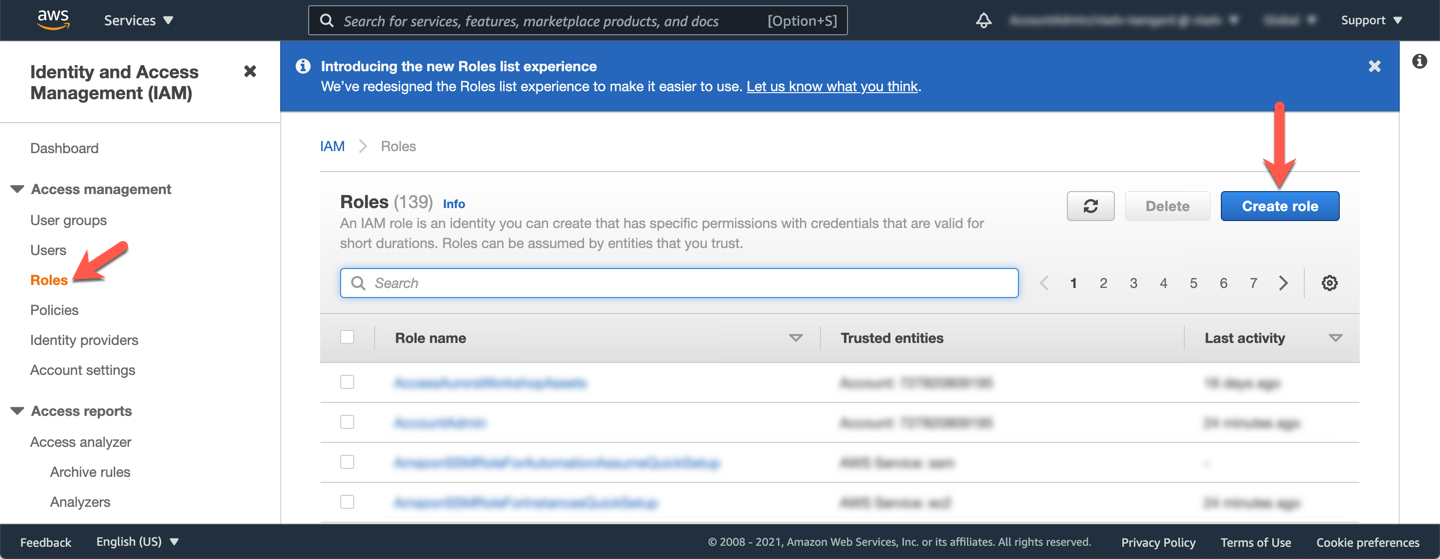
In the **Select type of trusted entity** section, choose **AWS service**. Next, in the **Choose the service that will use this role** section, choose **Lambda**, then click **Next: Permissions**.
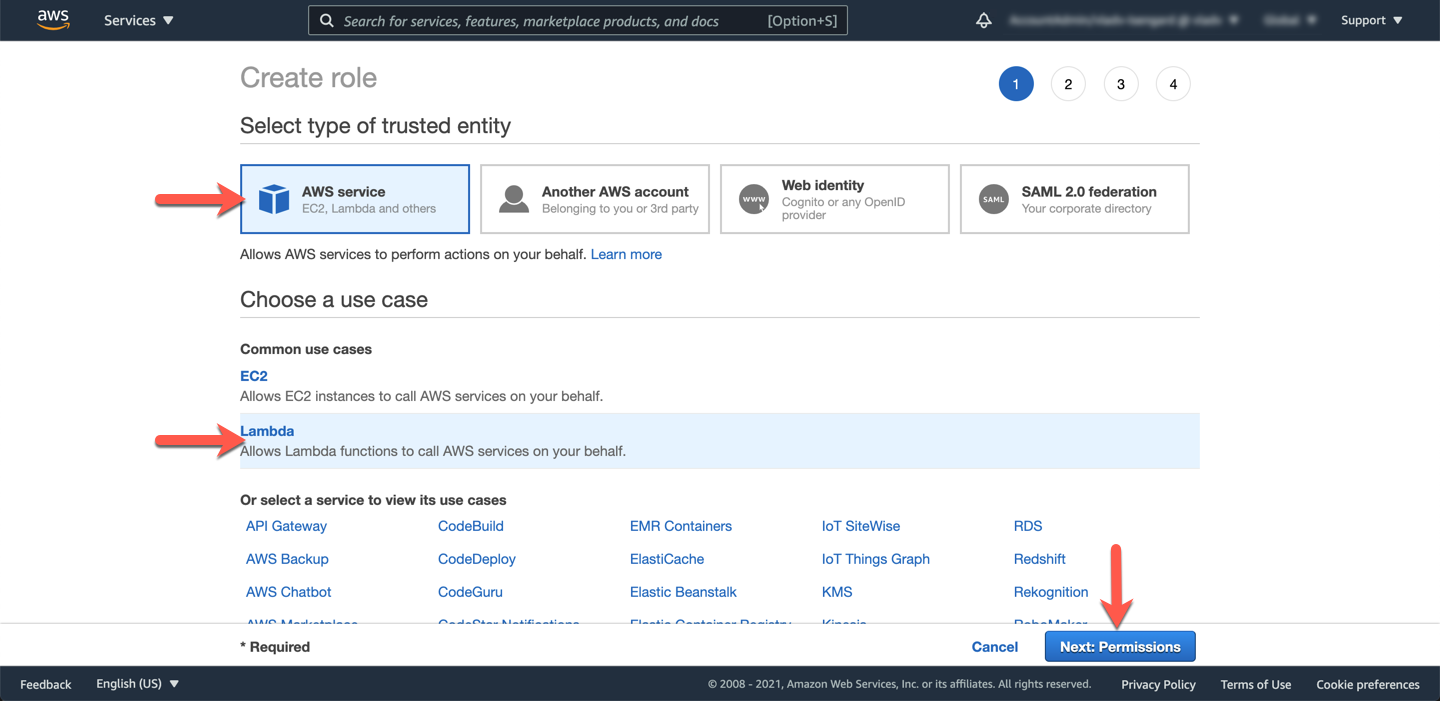
Click the **Create policy** button in the **Attach permissions policies** section.
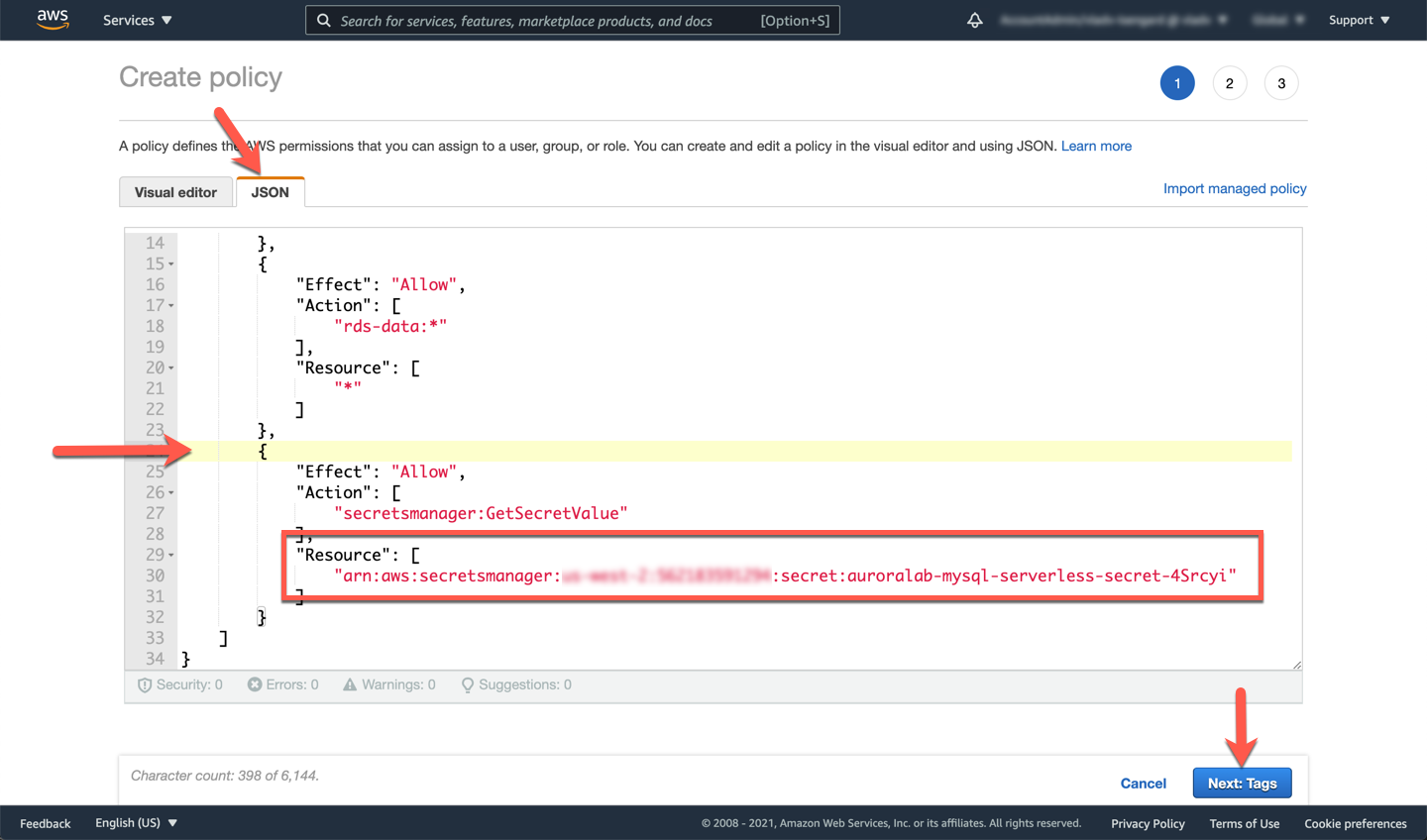
In the new browser tab that opens up, toggle to the **JSON** interface tab. Ignore any message that may be displayed warning that the policy validation failed - we have not created a policy yet. Paste the policy listed below in the text editor, and substitute the ==[SecretARN]== placeholder with the ARN of the secret you created in the previous lab. Click **Next: Tags**.
```
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"rds-data:*"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"secretsmanager:GetSecretValue"
],
"Resource": [
"[SecretARN]"
]
}
]
}
```
On the **Add tags (Optional)** screen, click **Next: Review**. Assign the IAM policy the name `auroralab-serverless-policy`, then click **Create policy**.
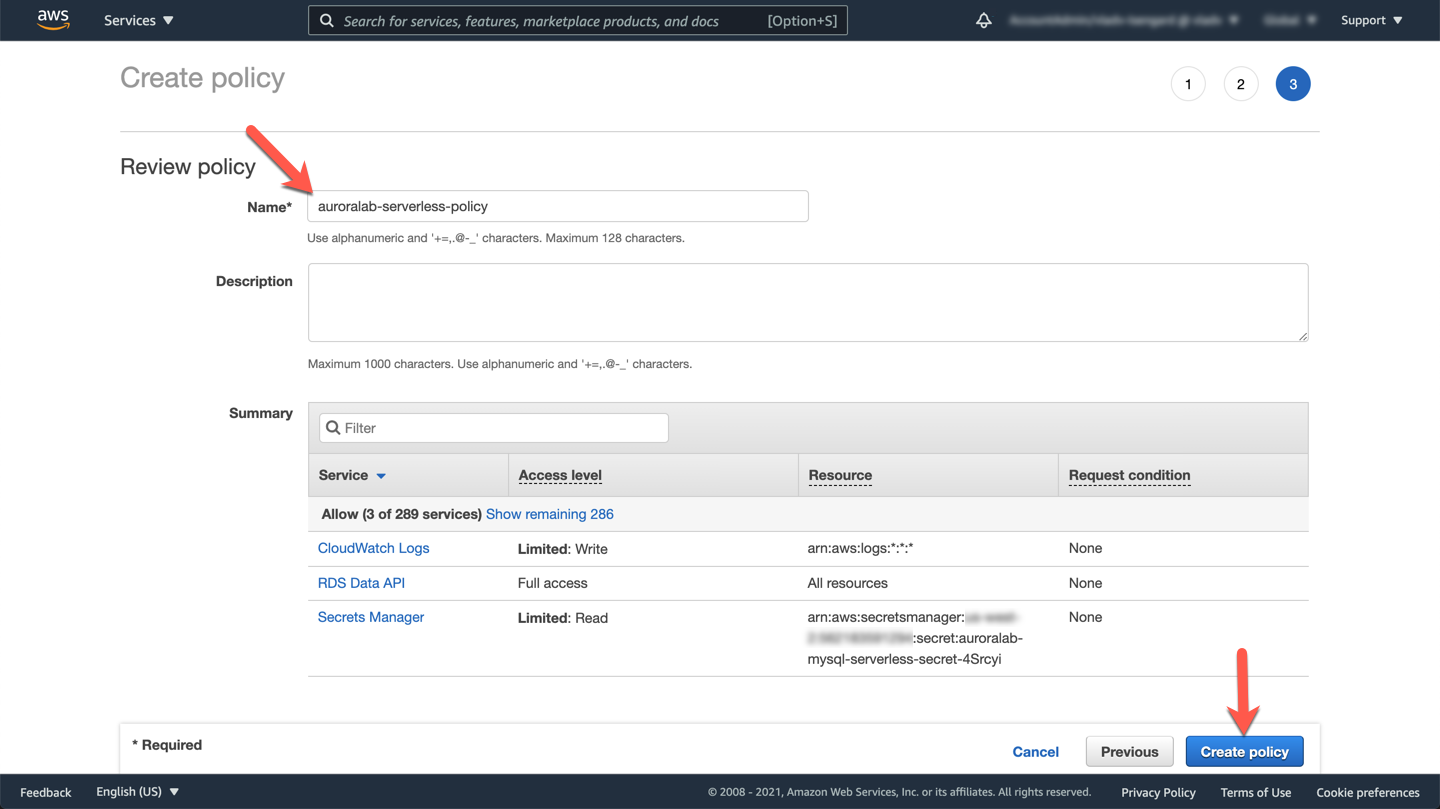
Once the policy has been created successfully, you can return to the other browser tab and continue configuring the role. You can also close the policy browser tab.
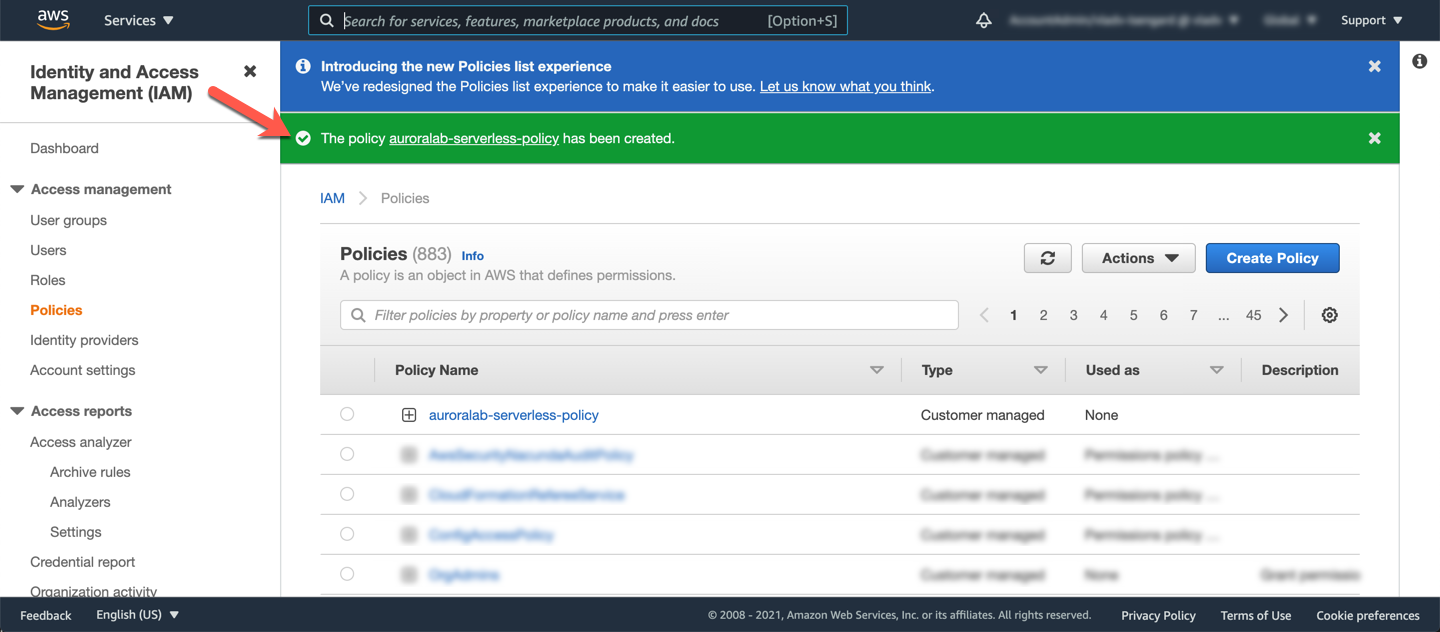
Back on the browser tab for creating the role, click the refresh icon in the top right of the policy list, then use the filter input field to search for the name of the policy you have just created. Select that policy, and click **Next: tags**.
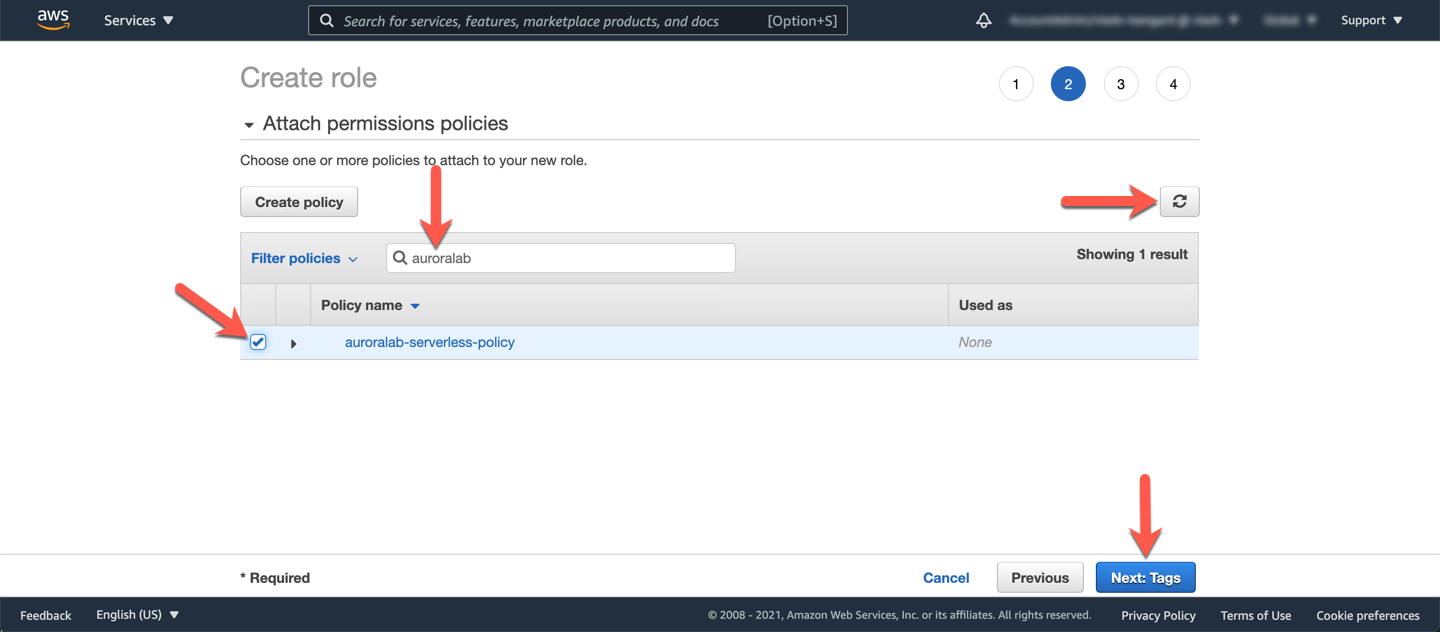
Skip the **Add tags** section, and click **Next: Review**. Then assign the role the name `auroralab-serverless-role`, and click **Create role**.
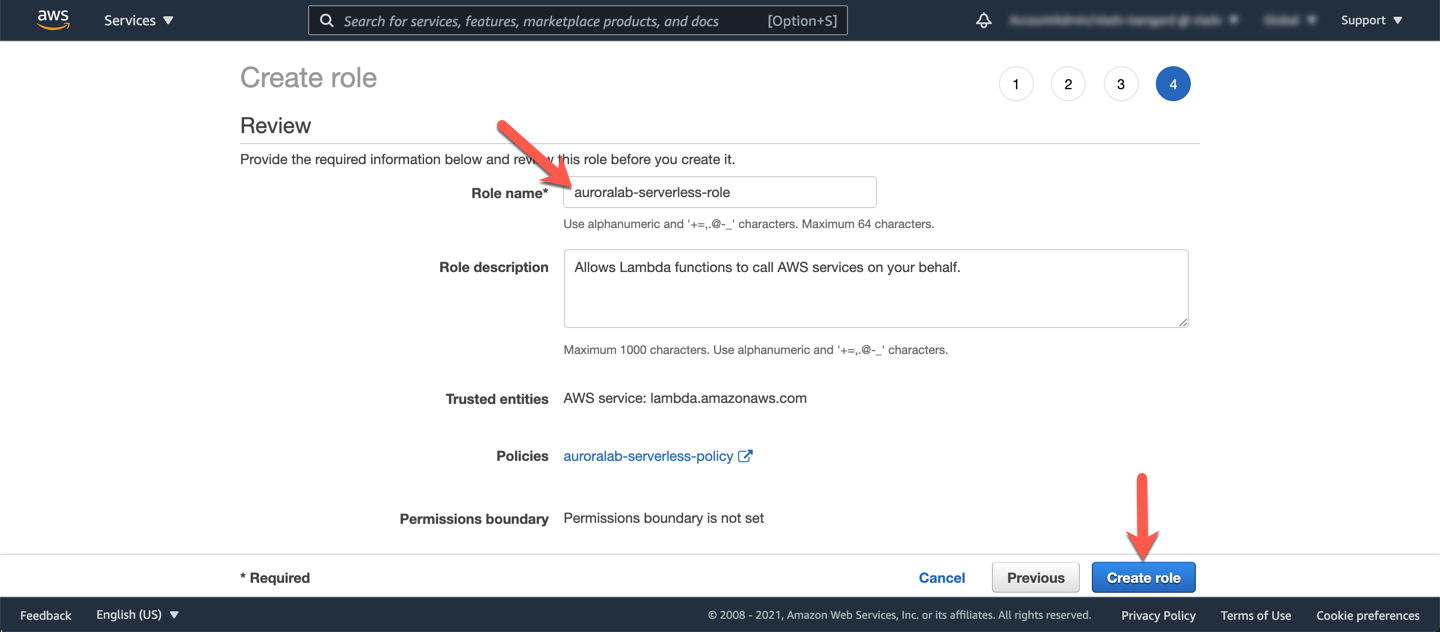
## 2. Create a Lambda function
Open the AWS Lambda service console.
Choose **Functions** from the left hand side menu, if it isn't already selected, and click **Create function**.
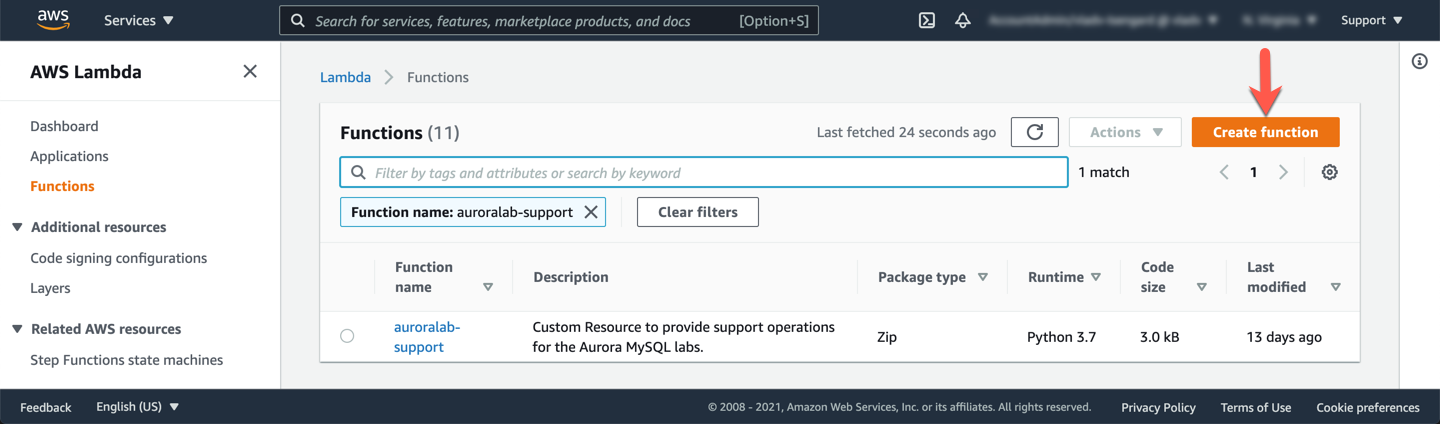
Choose the option to **Author from scratch**, set the **Function name** to `auroralab-serverless-function` and select **Node.js 14.x** for **Runtime**. Under **Permissions**, expand the sub-section called **Choose or create an execution role**. In the **Execution role** dropdown, select **Use an existing role**, then in the **Existing role** dropdown, select the execution role you have created previously, named `auroralab-serverless-role`. Click **Create function**.
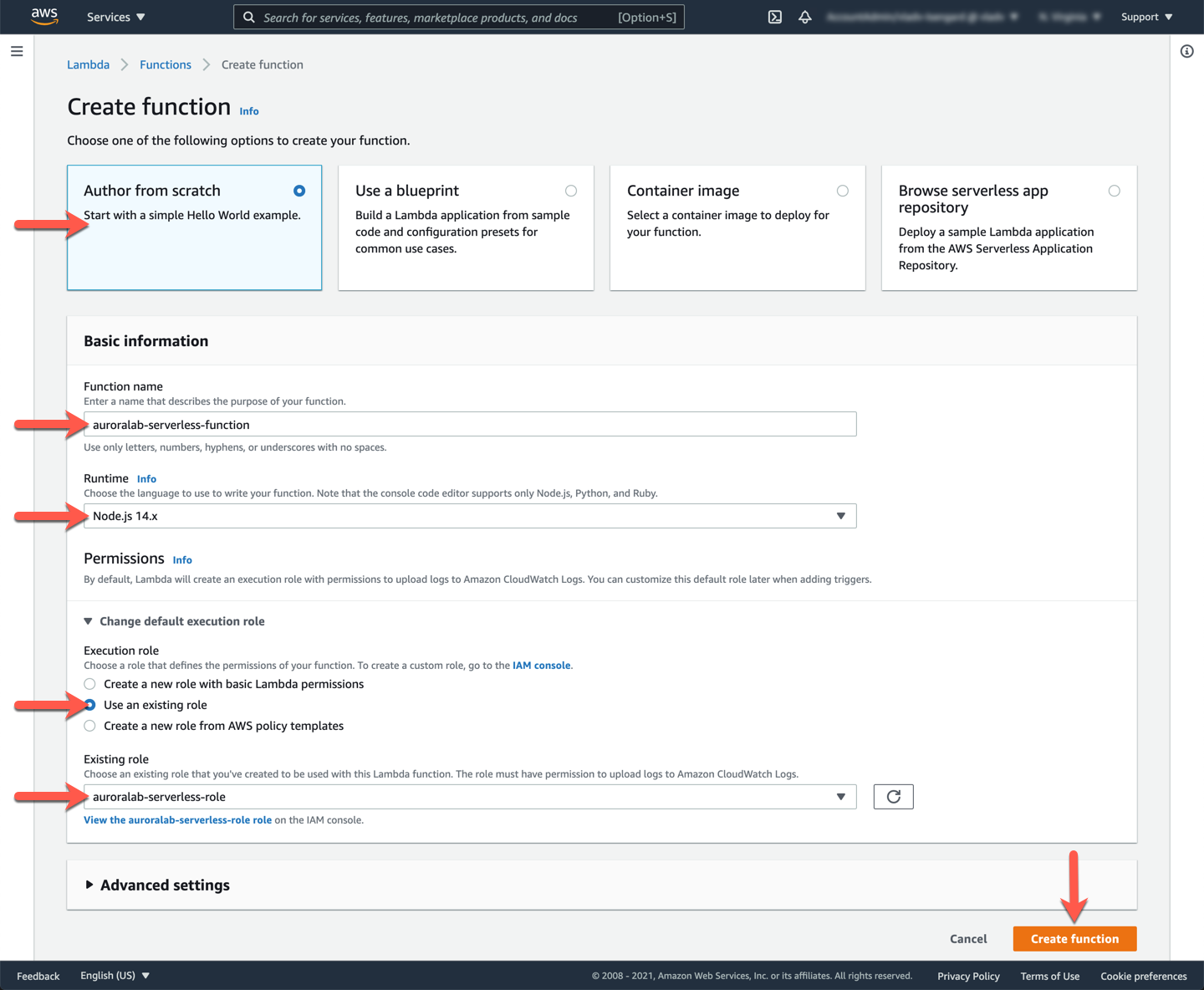
Make sure the **Code** tab is selected. In the **Code source** section, paste the code snipped below into the editor, and change the placeholders as follows:
Placeholder | Description | Where to find it
--- | --- | ---
==[ClusterARN]== | The ARN of the serverless database cluster resource. RDS Data API will establish connectivity with this database on your behalf. | See the previous lab: [Create an Aurora Serverless DB Cluster](/serverless/create/) at step *1. Create a serverless DB cluster*.
==[SecretARN]== | The ARN of the secret used to store the database credentials. RDS Data API will access this secret and connect to the database using those credentials. | See the previous lab: [Create an Aurora Serverless DB Cluster](/serverless/create/) at step *2. Create a secret to store the credentials*.
```
// require the AWS SDK
const AWS = require('aws-sdk')
const rdsDataService = new AWS.RDSDataService()
exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => {
// prepare SQL command
let sqlParams = {
secretArn: '[SecretARN]',
resourceArn: '[ClusterARN]',
sql: 'SHOW TABLES;',
database: 'information_schema',
includeResultMetadata: true
}
// run SQL command
rdsDataService.executeStatement(sqlParams, function (err, data) {
if (err) {
// error
console.log(err)
callback('Query Failed')
} else {
// init
var rows = []
var cols =[]
// build an array of columns
data.columnMetadata.map((v, i) => {
cols.push(v.name)
});
// build an array of rows: { key=>value }
data.records.map((r) => {
var row = {}
r.map((v, i) => {
if (v.stringValue !== "undefined") { row[cols[i]] = v.stringValue; }
else if (v.blobValue !== "undefined") { row[cols[i]] = v.blobValue; }
else if (v.doubleValue !== "undefined") { row[cols[i]] = v.doubleValue; }
else if (v.longValue !== "undefined") { row[cols[i]] = v.longValue; }
else if (v.booleanValue !== "undefined") { row[cols[i]] = v.booleanValue; }
else if (v.isNull) { row[cols[i]] = null; }
})
rows.push(row)
})
// done
console.log('Found rows: ' + rows.length)
callback(null, rows)
}
})
}
```
Click **Deploy** to save your code changes.
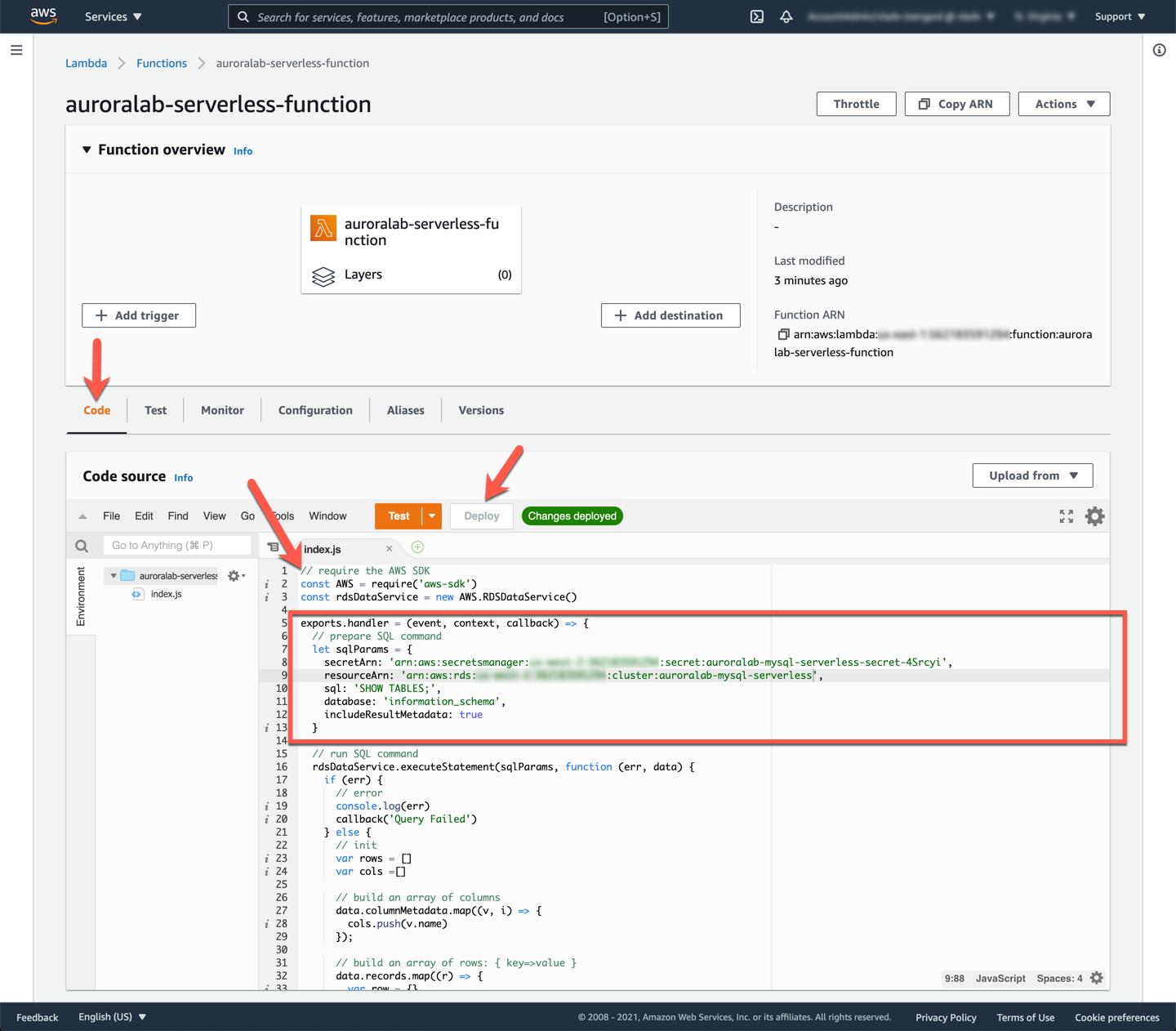
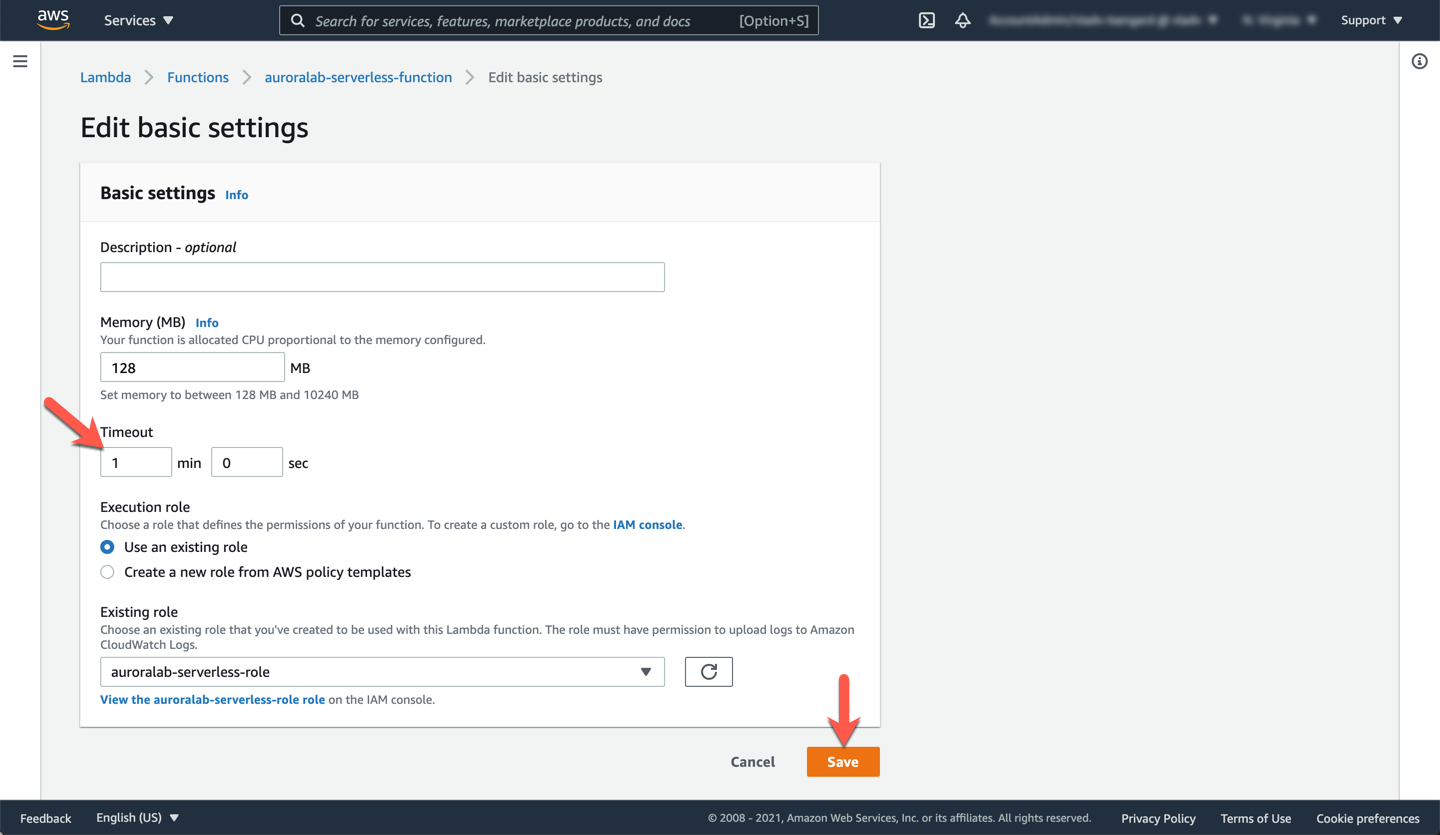
Switch to the **Configuration** tab. Choose **General configuration** from the left side menu, and click the **Edit** button.
Change the function **Timeout** to `1` min `0` sec, then click **Save**. We are increasing the timeout as it will take longer to respond to the first query against the serverless DB cluster. The compute capacity will be allocated only when the first request is received.
## 3. Connect to the database using the RDS Data API
Now you are ready to connect to the database from a Lambda function, by using the RDS Data API. The function doesn't bundle a database driver, it simply uses a RESTful AWS API call to send the SQL query: `SHOW TABLES;` and retrieves the result as a JSON data structure. This is accomplished in a minimal number of lines of code.
Switch back to the **Code** tab, and click the **Test** button in the **Code source** section.
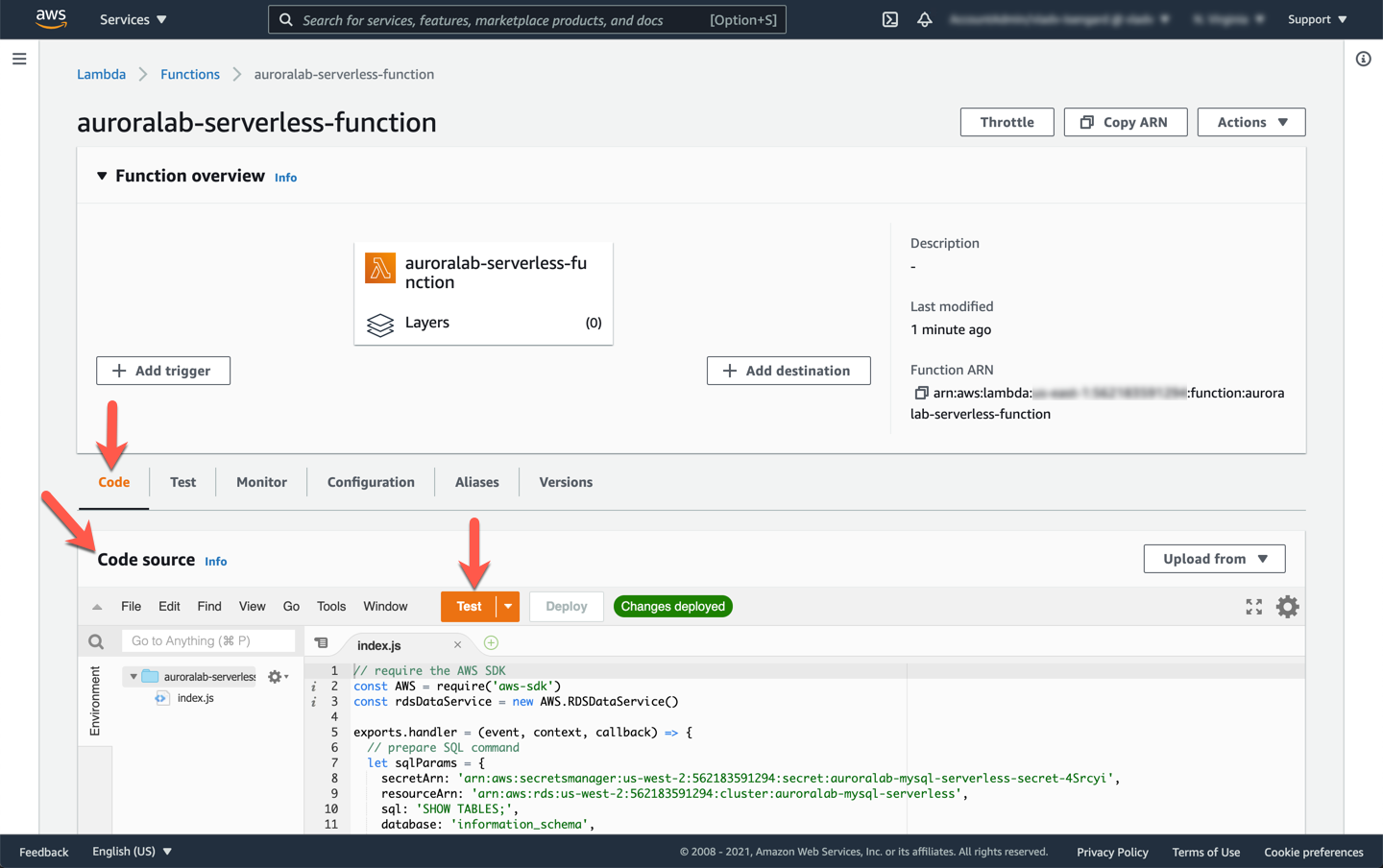
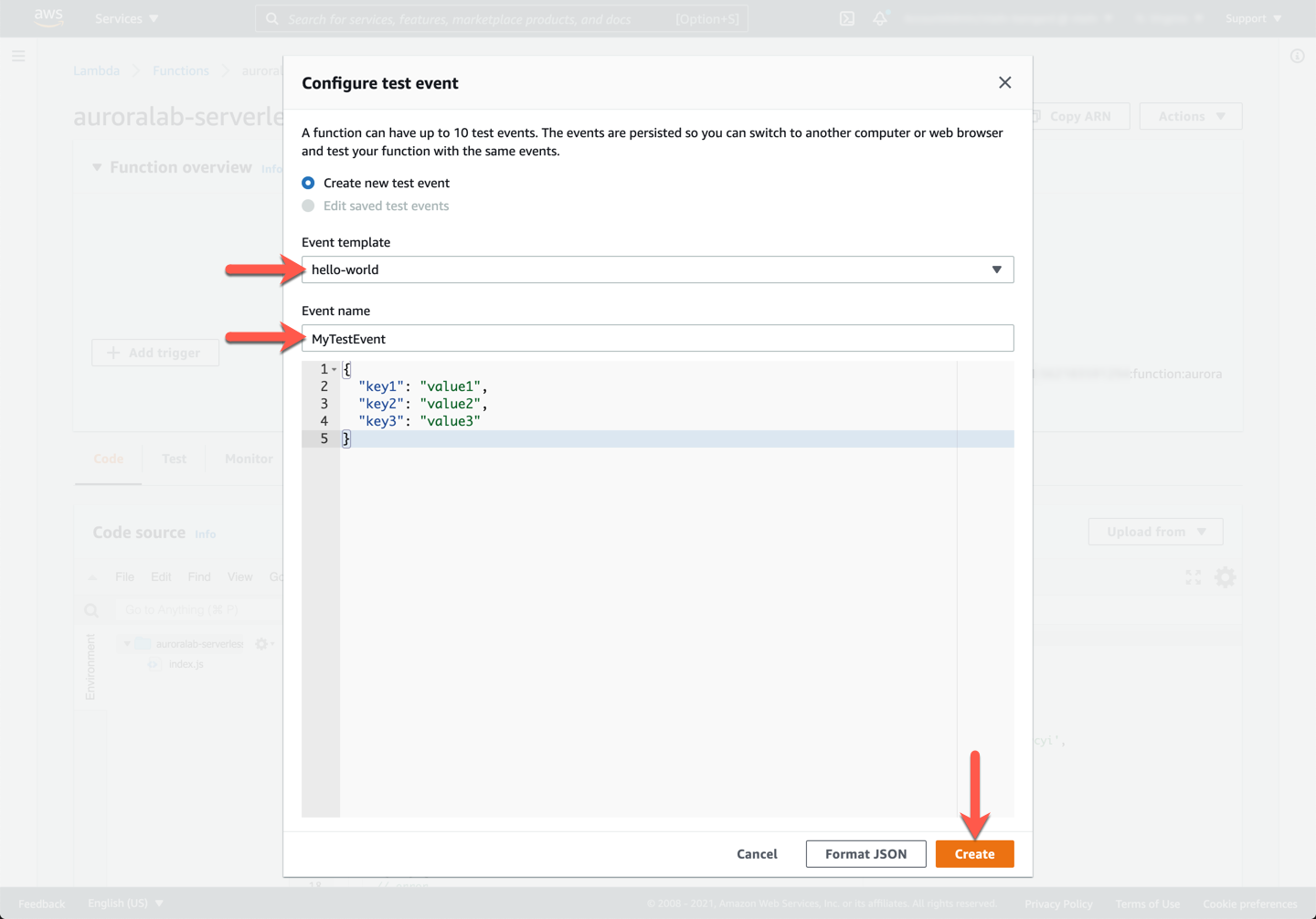
You will be asked to configure a test event the first time you try. The format and content for the test event are not relevant for this exercise, so pick any **Event template**, such as `Hello World`, input a memorable **Event name**, such as `MyTestEvent` and click **Create**.
If you have created a new test event, you may need to click the **Test** button again. After the function has completed running you can review the results, and see the function response. You may need to expand the **Details** sub-section of the **Execution result: succeeded** notification to see the results.
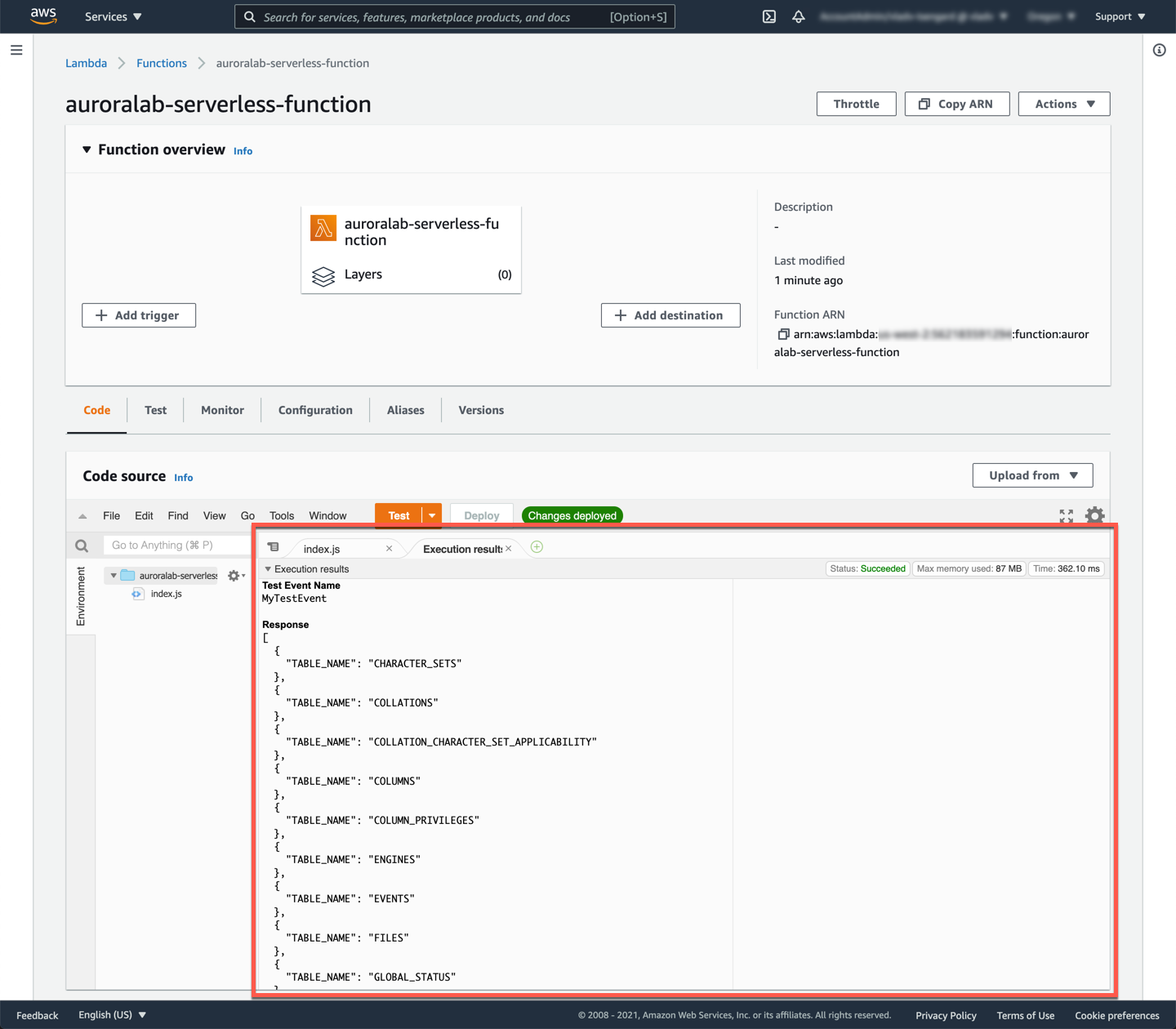
!!! note
Your first attempt to test the function may fail. In certain cases running the first command and activating the serverless DB cluster for the first time can take several seconds longer than the function or internal Data API timeouts. Try again and if you are still experiencing difficulties, notify one of the workshop support staff.