{
"cells": [
{
"attachments": {},
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "5bd5782c",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Method to help identify candidate features for RTS Consideration\n",
"\n",
"[Amazon Forecast](https://aws.amazon.com/forecast/) provides the ability to define and upload a special dataset type called [Related Time Series (RTS)](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/forecast/latest/dg/related-time-series-datasets.html) to help customers improve time-series model outcomes. RTS is a set of features that move in time, similar to the time movement of the Target Time Series (TTS) dataset. You may think of TTS as the dependent variable of the model and RTS as the independent variable(s). The goal of RTS is to help inform the model by explaining some of the variability in the dependent variable and produce a model with better accuracy.\n",
"\n",
"When customers use RTS, Amazon Forecast has a feature called [Predictor Explainability](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/forecast/latest/dg/predictor-explainability.html) which provides both visual and tabular feedback on which data features in the RTS were helpful to inform the model as shown in Figure 1.
\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"**Figure 1 - Built-in Predictor Explainability in Amazon Forecast**\n",
"\n",
"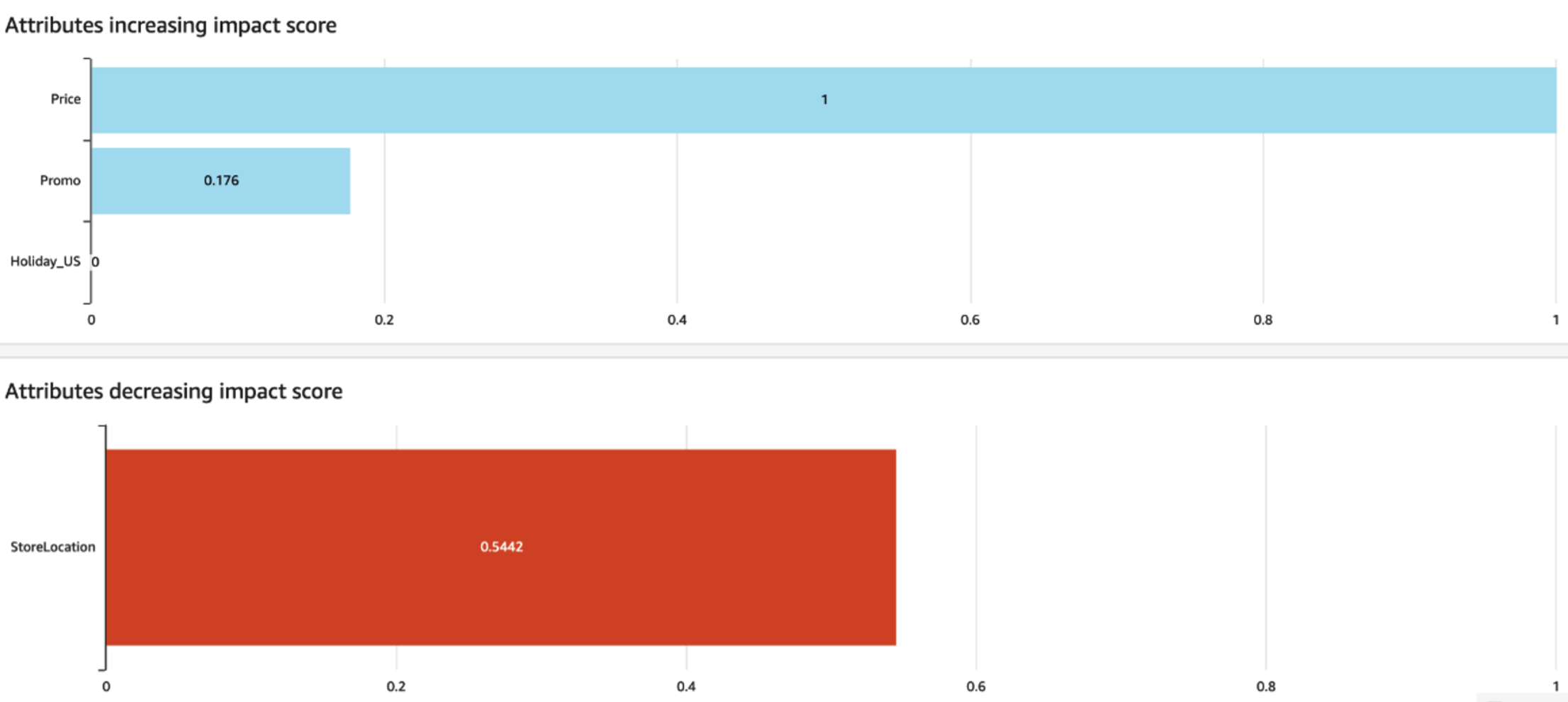 \n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"## Motivation for an exploratory candidate feature selection method\n",
"\n",
"Sometimes customers have dozens or hundreds of candidate features of interest and ask for a quick way to help reduce the set by finding features that are not significant. At the same time, a mutually exclusive secondary ask exists. Customers want a method to identify independent RTS features that exhibit collinearity. When candidate features in the RTS have a strong relationship, it can put the overall model at risk of overfitting. The goal here is to remove all but one of the strongly correlated values.\n",
"\n",
"There are many ways to accomplish these tasks of candidate selection. The goal is to find features that help explain the TTS target value, but not explain other RTS variables. This notebook provides rule-of-thumb guidance to assist with candidate selection. You may choose to use other methods in addition to this method. After having pared down the candidate set, you can create a new RTS set and import it into Amazon Forecast, where the [AutoPredictor](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/new-amazon-forecast-api-that-creates-up-to-40-more-accurate-forecasts-and-provides-explainability/) will give you more precise feedback. You can use the AutoPredictor metrics at the global or times-series level to understand if your proposed change was helpful and to what degree.\n",
"\n",
"Finally, to be explicit this notebook and candidate selection process has no temporal nature implied. This example simply compares the dependent and independent variables, **without time**, without sequence, and without any implied leads or lags."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "16ad6356",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Setup"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"id": "a7c9c8cb",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import pandas as pd\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"import statsmodels.api as sm\n",
"pd.options.display.float_format = '{:.3f}'.format"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "8265f656",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Import RTS Data\n",
"\n",
"This section will load RTS data from an open-source data set and generate features that should be flagged by the candidate selection proposed."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 2,
"id": "e5663e5f",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"(456547, 4)\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"rts_column_list = [\"location_id\",\"item_id\",\"checkout_price\",\"base_price\",\n",
" \"emailer_for_promotion\",\"homepage_featured\",\"timestamp\"]\n",
"\n",
"rts_dtype_dic= { \"location_id\":str,\"item_id\":str,\"checkout_price\":float,\"base_price\":float,\n",
" \"emailer_for_promotion\":float,\"homepage_featured\":float,\"timestamp\":str}\n",
"\n",
"rts_index = ['timestamp','location_id','item_id']\n",
"\n",
"rts = pd.read_csv('./data/food-forecast-rts-uc1.csv',\n",
" index_col=rts_index,\n",
" skiprows=1,\n",
" names=rts_column_list,\n",
" dtype = rts_dtype_dic\n",
" )\n",
"print(rts.shape) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "831f37f9",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Next, features will be created to ensure they are flagged for low importance and collinearity:\n",
"- feature X1 is created to simulate noise, via a random function\n",
"- feature X2 is created to be highly correlated to base price\n",
"- feature X3 is an engineered feature to inform discounted sales price"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 3,
"id": "41806bd8",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# seed the pseudorandom number generator\n",
"from random import seed\n",
"from random import random\n",
"# seed random number generator\n",
"seed(42)\n",
"rts['x1'] = [np.random.normal() for k in rts.index]\n",
"rts['x2'] = rts['base_price']*0.9\n",
"rts['x3'] = rts['checkout_price']/rts['base_price']"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "9d68e669",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Preview the RTS "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 4,
"id": "eaf2ac34",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/html": [
"\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" checkout_price | \n",
" base_price | \n",
" emailer_for_promotion | \n",
" homepage_featured | \n",
" x1 | \n",
" x2 | \n",
" x3 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | timestamp | \n",
" location_id | \n",
" item_id | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | 2018-10-16 | \n",
" 10 | \n",
" 1062 | \n",
" 157.140 | \n",
" 157.140 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.053 | \n",
" 141.426 | \n",
" 1.000 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2018-10-30 | \n",
" 10 | \n",
" 1062 | \n",
" 158.170 | \n",
" 156.170 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" -1.791 | \n",
" 140.553 | \n",
" 1.013 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2017-12-05 | \n",
" 10 | \n",
" 1062 | \n",
" 159.080 | \n",
" 182.390 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.387 | \n",
" 164.151 | \n",
" 0.872 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2017-03-21 | \n",
" 10 | \n",
" 1062 | \n",
" 159.080 | \n",
" 183.330 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" -0.658 | \n",
" 164.997 | \n",
" 0.868 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2017-06-20 | \n",
" 10 | \n",
" 1062 | \n",
" 159.080 | \n",
" 183.360 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" 0.000 | \n",
" -0.217 | \n",
" 165.024 | \n",
" 0.868 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" | \n",
" target_value | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | timestamp | \n",
" location_id | \n",
" item_id | \n",
" | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | 2016-11-08 | \n",
" 55 | \n",
" 1993 | \n",
" 270.000 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2539 | \n",
" 189.000 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2139 | \n",
" 54.000 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 2631 | \n",
" 40.000 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 1248 | \n",
" 28.000 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | \n",
" significant | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | variable | \n",
" | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | x1 | \n",
" 181 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"
On the other hand; below, these fields appear significant in at least 20% or more series. Change the threshold as appropriate for your use case."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 10,
"id": "37dba986",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"text/html": [
"\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | \n",
" significant | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | variable | \n",
" | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | emailer_for_promotion | \n",
" 2052 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | homepage_featured | \n",
" 2125 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | x3 | \n",
" 2353 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | checkout_price | \n",
" 2888 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | base_price | \n",
" 3115 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | x2 | \n",
" 3115 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | \n",
" index | \n",
" variable | \n",
" coefficient | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
" \n",
" | 3 | \n",
" base_price | \n",
" x2 | \n",
" 1647 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 11 | \n",
" checkout_price | \n",
" x3 | \n",
" 2386 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 15 | \n",
" emailer_for_promotion | \n",
" x3 | \n",
" 811 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 34 | \n",
" x2 | \n",
" base_price | \n",
" 1321 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 42 | \n",
" x3 | \n",
" emailer_for_promotion | \n",
" 808 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" | 44 | \n",
" x3 | \n",
" target_value | \n",
" 720 | \n",
"
\n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"