## Deployment
### Prerequisites
* [Node.js version 12.0.0 or later](https://nodejs.org/) to run Node scripts
* [AWS account](https://aws.amazon.com/) to create resources
* [AWS CLI version 2](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/install-cliv2.html) to run scripts
* [Git Bash](https://git-scm.com/) to run Bash scripts (only on Windows)
* [Docker version 20.10.5 or later](https://www.docker.com/) and Docker daemon up and running to build and push ECS container images
### 1) Assign random suffix to resource names
Run `bash assign-random-suffix.sh`.
This will generate a 6 character length alphanumeric value. Then, it will update the [cloudformation.yaml](./cloudformation.yaml) file and bash script files by replacing the placeholder ``, located at the end of the resource names, with the random value generated to ensure uniqueness.
> **Note:**
> There is no script to reverse this step, but you can use Git to discard all changes and go back to the original state.
### 2) Configure AWS CLI
Run `aws configure` to set your credentials and the region where you want the demo resources deployed.
### 3) Change Transcribe language (optional)
You can change the default Transcribe language (English) by modifying the following parameters in the [cloudformation.yaml](./cloudformation.yaml) file:
* **AudioLanguageCode**: ISO 639-1 code of the audio language to be transcribed, you can find the corresponding code [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_ISO_639-1_codes).
* **AudioLanguageTranscribeCode**: Amazon Transcribe code of the audio language to be transcribed, you can find the corresponding code [here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/transcribe/latest/dg/supported-languages.html).
> **Notes:**
> * This demo supports *overlays*, *custom vocabulary* and *vocabulary filter* functionalities only for **English transcriptions**.
> * Captions are built using *partials* only with **English transcriptions**, which allows 2 rows of captions to be displayed at a time and in a constant manner. For any other language, captions are built using *totals*, hence they will be displayed with less frequency and may span across more than 2 rows.
### 4) Configure Translate language(s) (optional)
When the deployment script starts execution, you will be prompted for confirmation on whether to enable the **Translate** feature or not. If enabled, the transcription generated by Amazon Transcribe will be translated by Amazon Translate to the configured language(s). On the player you will be able to switch between the Transcribe language (transcribed audio) and the Translate language(s) (transcription translation(s)) for captions, by clicking on the gear icon. Any [Amazon Translate](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/translate/latest/dg/what-is.html) supported language can be enabled by modifying the [Translate Languages file](./translate-languages.json) and setting the desired translation language(s) value to **true**.
> **Note:**
> Captions are built using *partials* only with **English transcriptions**, which allows 2 rows of captions to be displayed at a time and in a constant manner. For translations, captions are built using *totals*, hence they will be displayed with less frequency and may span across more than 2 rows.
### 5) Run deployment script
Run `bash deploy.sh`.
This will deploy the demo infrastructure. **Only if the Transcribe language is English**, the following configurations will be performed at the end of the deployment process, using the already provided default values:
* [Overlays](../configuration/README.md#configure-overlays)
* [Custom vocabulary](../configuration/README.md#configure-custom-vocabulary)
* [Vocabulary filter](../configuration/README.md#configure-vocabulary-filter)
> **Note:**
> On MacOS, some steps of the deployment show large outputs that require you to press "q" to continue with the deployment execution.
In case of failure, check the script outputs and the CloudFormation console. Common issues are:
* The Docker daemon is not running (check [how to configure and troubleshoot the Docker daemon](https://docs.docker.com/config/daemon/))
* A service quota has been reached (check [AWS service quotas](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/aws_service_limits.html))
After solving the issue, run the cleanup script and then the deployment script again (some error messages stating that the resources could not be deleted may arise during the cleanup process if the deployment was made partially).
## Usage
At the end of the deploy.sh execution, you will see the following output in the console:
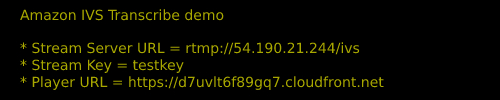
Use the **Stream Server URL** and the **Stream Key** values to configure your streaming tool (we are using [OBS](https://obsproject.com/) in this example):
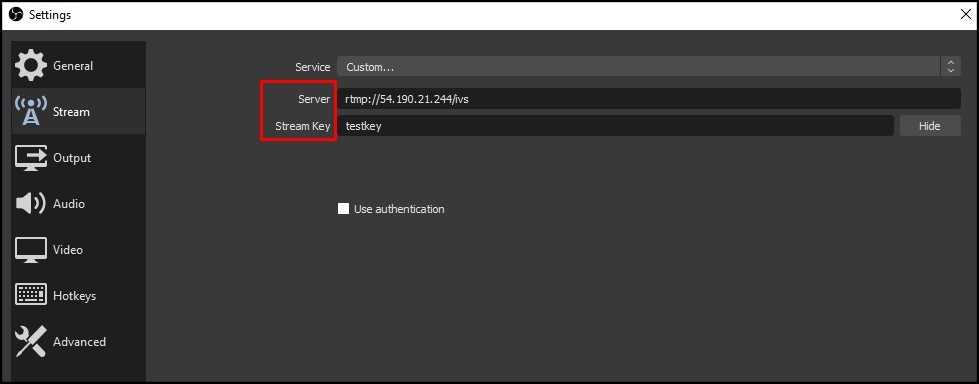
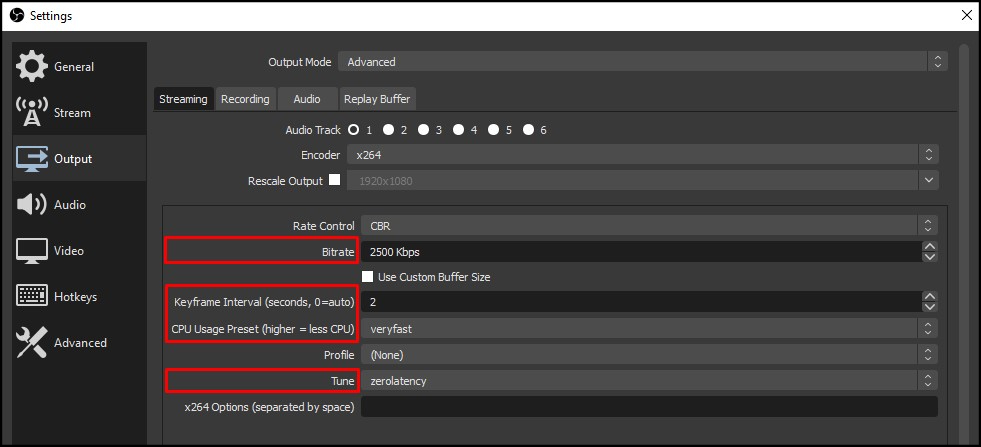
Check that you have the following Output settings:
* **Bitrate:** `2500 Kbps`
* **Keyframe Interval:** `2`
* **CPU Usage:** `veryfast`
* **Tune:** `zerolatency`
Open up the player using the **Player URL** value provided in the console output:
Optionally, you can configure [certain aspects of the demo](../configuration/README.md).
## Cleanup
Run `bash cleanup.sh`.
This will remove all the resources created during the execution of `deploy.sh`.
## Scripts included in this folder
This section includes details of every script present in this folder for informational purposes, you need only to run the scripts described in the **Deployment** and **Cleanup** sections above.
### generate-player-app-env-vars.js
Creates a file with the environment variables for the player-app, after obtaining them from the output file of the CloudFormation deployment (i.e. `stack.json`). This script is called by the [deploy-player-app.sh](#deploy-player-appsh) script.
Parameters:
1) STACK_FILE_PATH (required)
Example:
```shell
node generate-player-app-env-vars.js stack.json
```
### deploy-player-app.sh
Calls the [generate-player-app-env-vars.js](#generate-player-app-env-varsjs) script to create the .env file with the corresponding environment variables. Then, the required dependencies are installed and the application is built using the previously generated environment variables. Finally, the build files are uploaded to an S3 bucket. This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script.
Parameters:
1) STACK_FILE_PATH (required)
Example:
```shell
bash deploy-player-app.sh stack.json
```
### setup-images.sh
Creates 2 repositories in the Amazon ECS private registry to host the Stream and Transcribe containers images. Then, logs in into the registry and uses the [Stream Dockerfile](../serverless/stream-server/Dockerfile) and [Transcribe Dockerfile]((../serverless/stream-server/Dockerfile)) to build and push the corresponding images. This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script.
Parameters: None
Example:
```shell
bash setup-images.sh
```
### setup-lambdas.sh
Generates a zip file for each Lambda function located within the [serverless folder](../serverless) by calling the [zip-generator.js](#zip-generatorjs) script. Then, creates an S3 bucket and uploads the Lambda functions zip files into it. This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script.
Parameters: None
Example:
```shell
bash setup-lambdas.sh
```
### create-stack.sh
Creates the CloudFormation stack using the specified stack name and the [cloudformation.yaml file](./cloudformation.yaml). This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script.
Parameters:
1) STACKNAME (required)
Example:
```shell
bash create-stack.sh ivs-transcribe-demo-stack
```
### zip-generator.js
Generates a zip file for each specified folder. This script is called by the [setup-lambdas.sh](#setup-lambdassh) script.
Parameters:
* FOLDER_PATH (variable)
Example:
```shell
node zip-generator.js ../serverless/lambda-on-connect ../serverless/lambda-on-disconnect ../serverless/lambda-send-transcription
```
### deploy.sh
Main script used to perform the demo deployment. It calls the following scripts:
1) [setup-lambdas.sh](#setup-lambdassh)
2) [setup-images.sh](#setup-imagessh)
3) [create-stack.sh](#create-stacksh)
4) [deploy-player-app.sh](#deploy-player-appsh)
5) [configure-all.sh](../configuration/README.md#configure-allsh) (only if Transcribe language is English)
6) [generate-output.js](#generate-outputjs)
Parameters: None
Example:
```shell
bash deploy.sh
```
### cleanup.sh
Removes all the demo resources that were created by [deploy.sh](#deploysh).
Parameters: None
Example:
```shell
bash cleanup.sh
```
### assign-random-suffix.sh
Generates a 6 character length alphanumeric value and assigns it to every `` placeholder located in the following files:
* [configure-all.sh](../configuration/configure-all.sh)
* [configure-custom-vocabulary.sh](../configuration/configure-custom-vocabulary.sh)
* [configure-overlays.sh](../configuration/configure-overlays.sh)
* [configure-vocabulary-filter.sh](../configuration/configure-vocabulary-filter.sh)
* [create-custom-vocabulary.sh](../configuration/create-custom-vocabulary.sh)
* [create-vocabulary-filter.sh](../configuration/create-vocabulary-filter.sh)
* [setup-images.sh](./setup-images.sh)
* [setup-lambdas.sh](./setup-lambdas.sh)
* [deploy-player-app.sh](./deploy-player-app.sh)
* [cleanup.sh](./cleanup.sh)
* [cloudformation.yaml](./cloudformation.yaml)
Parameters: None
Example:
```shell
bash assign-random-suffix.sh
```
### generate-output.js
Generates the outputs needed to run the demo, specifically:
* **Stream Server URL**
* **Stream Key**
* **Player URL**
To retrieve the values, it uses the CloudFormation *stack.json* output file and the AWS SDK. This script is called by [deploy.sh](#deploysh) after deploying all the needed resources.
Parameters:
* `--stackOutputFilePath`: Path to CloudFormation output file (required).
Example:
```shell
node generate-output.js --stackOutputFilePath stack.json
```
### delete-api-stages.js
Deletes the **demo** stage created for both API Gateways (Reader WebSocket and Writer WebSocket). This script is called by the [cleanup.sh](#cleanupsh) script prior to remove the stack.
Parameters:
* `--stackOutputFilePath`: Path to CloudFormation output file (required).
Example:
```shell
node delete-api-stages.js --stackOutputFilePath stack.json
```
### get-audio-language-code.js
Retrieves the **AudioLanguageCode** CloudFormation parameter value from the stack output file (*stack.json*). This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script to check the audio language. If the code is **en** (English) the overlays, custom vocabulary and vocabulary filter configurations are performed with the provided default values; if the code is not **en**, configurations are not performed.
Parameters:
* `--stackOutputFilePath`: Path to CloudFormation output file (required).
Example:
```shell
node get-audio-language-code.js --stackOutputFilePath stack.json
```
### get-translate-languages.js
Retrieves the configured Translate languages codes (i.e. the codes between brackets within the keys that have the value **true** in the [Translate Languages file](./translate-languages.json)) and outputs them as comma-separated values. The script assumes the Translate languages file is located in the same directory. This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script.
Parameters: None
Example:
```shell
node get-translate-languages.js
```
### validate-translate-config.js
Validates that the Translate configuration is correct:
* There is at least one Translate language enabled
* There is no Translate language equal to the Transcribe language
* Translate languages have been retrieved correctly
The script assumes the CloudFormation template file is located in the same directory. This script is called by the [deploy.sh](#deploysh) script.
Parameters:
* TRANSLATE_LANGUAGES: Enabled Translate language codes as a list of comma-separated values (required).
Example:
```shell
node validate-translate-config.js
```