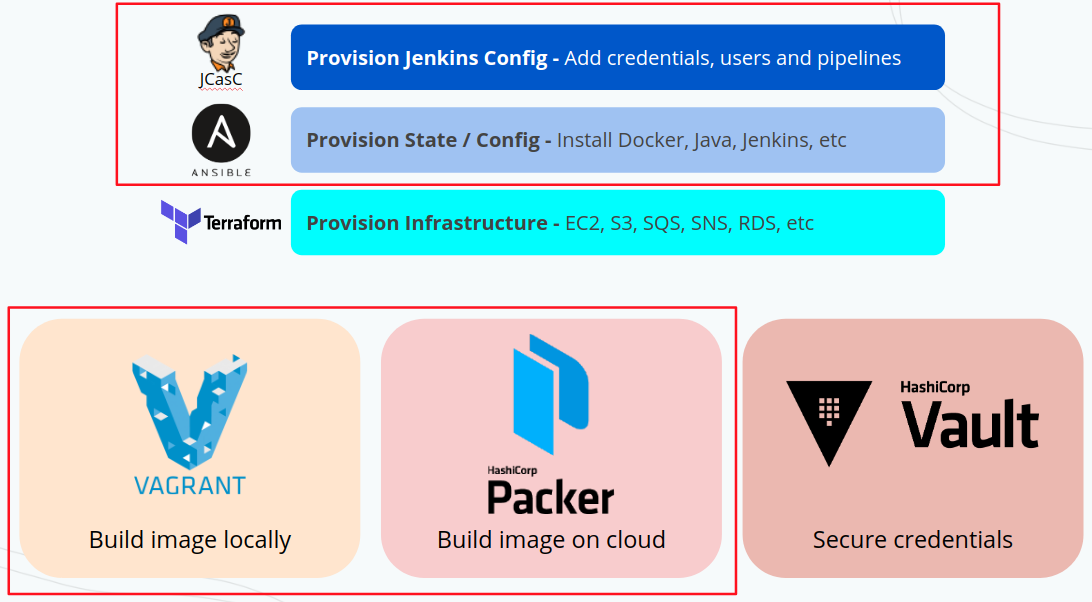
## 2. Customizing this repo: configuring Jenkins and creating your pipelines
```
Copyright Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT-0
```
This project has configurations for Jenkins with Terraform, Ansible, SSM, AWS CLI, Java, and HAProxy (for TLS activation). You can change all this configuration on file ansible_config/site.yml. More information on roles on the last part of this readme.
### Jenkins configuration files
1. This jenkins is configured automatically using Jenkins plugin configuration as code. All the configuration is listed on file jenkins.yaml available in ansible_config/roles/ansible-role-jenkins/files/jenkins.yaml. On that file you can add your pipelines and credentials for those pipelines to consume. Full documentation and possibilities can be found here.
2. To set your own pipelines as code, check the file ansible_config/roles/ansible-role-jenkins/files/jenkins.yaml. There you're going to find same examples about credentials mapping and one example pipeline. For more documentation on how to write pipelines as code, please refer to https://localhost:5555/plugin/job-dsl/api-viewer/index.html
3. The plugins that this Jenkins will have installed can be found at: ansible_config/roles/ansible-role-jenkins/defaults/main.yml. If you need to get your current installed plugins, you can find how to here.
4. You can change jenkins default admin password on file ansible_config/roles/ansible-role-jenkins/defaults/main.yml attribute "jenkins_admin_password"
### 2.1. Using Packer to build your AMI
Packer is a tool to create an OS image
Running packer (pending):
1. packer build -var AWS_USER_CREDS_HERE packer_config.json
2. Once you have your AMI created, go for your cloud console and create a new machine pointing to the newly created image.
Checkout the file packer_config.json to see how packer will create your SO image and AWS instructions for it
PS: This specific packer_config.json file is configured to create an image on AWS. You can change it to run on AWS if you have to.
IMPORTANT for SECURITY: If you are building for production environment go to file ansible_config/roles/ansible-role-jenkins/defaults/main.yaml and uncomment lines - option: "JENKINS_ARGS" and value: "--httpListenAddress=127.0.0.1"
Once done, your Jenkins will stop answering for all requests that don't come through HAProxy, and therefore will only accept https requests and deny all the others. If you still have to allow this access, after everything is set up, ssh into the created machine and change the "127.0.0.1" in the very end of file /etc/default/jenkins to "0.0.0.0" and restart jenkins service.
## 2.2. Understanding Ansible
Ansible is a tool to configure our OS as we want it to be.
You can run ansible with: ansible playbook site.yml. See examples at Vagrantfile and packer_config.json
The main file for this folder is ansible_config/site.yml. This file calls all the roles in "roles" folder
### Ansible roles:
The roles folder has the Ansible configuration for:
1. Add Java PPA
2. Role - Install Java JDK 8
3. Role - Install Terraform
4. Role - Install Ansible
5. Role - AWS CLI
6. Role - Commons
7. Role - Install Jenkins (with plugins and pipelines configuration)
8. Role - Install HAProxy to handle the server TLS
## 2.3. Activating TLS (https)
### 2.3.1 - TLS: Once you have your machine up and running, connect through SSH
1. Check if the AMI image you built to install Jenkins has the option to activate TLS set while running the playbook (variable activate_tls_only on ansible-role-haproxy).
2. Change the configurations on file ansible_config/roles/ansible-role-haproxy/templates/haproxy-tls.cfg to point to your company's URL instead of "jenkins.mycompany.com"
3. Having your company certificates handy, generate the .pem certificate file with command cat STAR.mycompany.com.crt STAR.mycompany.com.key > fullkey.pem. Remember to remove the empty row that is kept inside the generated fullkey.pem between the two certificates. To look at the file use cat fullkey.pem
4. Move the generated file to your running instance's folder /home/centos/jenkins/
5. Restart HAProxy with sudo service haproxy restart
IMPORTANT: If you changed the file /etc/default/jenkins to IP 0.0.0.0, put it back to 127.0.0.1 otherwise Jenkins will still accept connections from non-https requests
Done! Your Jenkins is ready to run under https with valid certificates. Just point your DNS to the running machine and you're done.
## 2.4. More about this project
This project covers the following tools: