# Ingesting data into a collection using Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion

This is an Amazon OpenSearch ingestion project for CDK development with Python.
This project builds on the following tutorial: [Ingesting data into a collection using Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/osis-serverless-get-started.html).
This project shows you how to use Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion to configure a simple pipeline and ingest data into an Amazon OpenSearch Serverless collection.
The `cdk.json` file tells the CDK Toolkit how to execute your app.
This project is set up like a standard Python project. The initialization
process also creates a virtualenv within this project, stored under the `.venv`
directory. To create the virtualenv it assumes that there is a `python3`
(or `python` for Windows) executable in your path with access to the `venv`
package. If for any reason the automatic creation of the virtualenv fails,
you can create the virtualenv manually.
To manually create a virtualenv on MacOS and Linux:
```
$ python3 -m venv .venv
```
After the init process completes and the virtualenv is created, you can use the following
step to activate your virtualenv.
```
$ source .venv/bin/activate
```
If you are a Windows platform, you would activate the virtualenv like this:
```
% .venv\Scripts\activate.bat
```
Once the virtualenv is activated, you can install the required dependencies.
```
(.venv) $ pip install -r requirements.txt
```
At this point you can now synthesize the CloudFormation template for this code.
(.venv) $ export CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query Account --output text)
(.venv) $ export CDK_DEFAULT_REGION=$(curl -s 169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document | jq -r .region)
(.venv) $ cdk synth -c iam_user_name=your-iam-user-name --all
:warning: Amazon OpenSearch Serverless requires mandatory IAM permission for access to resources.
You are required to add these two IAM permissions for your OpenSearch Serverless **"aoss:APIAccessAll"** for Data Plane API access, and **"aoss:DashboardsAccessAll"** for Dashboards access. Failure to add the two new IAM permissions will result in 403 errors starting on May 10th, 2023
For a sample data-plane policy [here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/security-iam-serverless.html#security_iam_id-based-policy-examples-data-plane.html):
- [Using OpenSearch Serverless in the console
](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/security-iam-serverless.html#security_iam_serverless_id-based-policy-examples-console)
- [Administering OpenSearch Serverless collections](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/security-iam-serverless.html#security_iam_id-based-policy-examples-collection-admin)
- [Viewing OpenSearch Serverless collections](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/security-iam-serverless.html#security_iam_id-based-policy-examples-view-collections)
- [Using data-plane policies](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/security-iam-serverless.html#security_iam_id-based-policy-examples-data-plane)
Use `cdk deploy` command to create the stack shown above.
(.venv) $ cdk deploy -c iam_user_name=your-iam-user-name --all
To add additional dependencies, for example other CDK libraries, just add
them to your `setup.py` file and rerun the `pip install -r requirements.txt`
command.
## Clean Up
Delete the CloudFormation stack by running the below command.
(.venv) $ cdk destroy -c iam_user_name=your-iam-user-name --force --all
## Useful commands
* `cdk ls` list all stacks in the app
* `cdk synth` emits the synthesized CloudFormation template
* `cdk deploy` deploy this stack to your default AWS account/region
* `cdk diff` compare deployed stack with current state
* `cdk docs` open CDK documentation
Enjoy!
## Run Tests
#### Step 1: Ingest some sample data
First, get the ingestion URL from the **Pipeline settings** page:
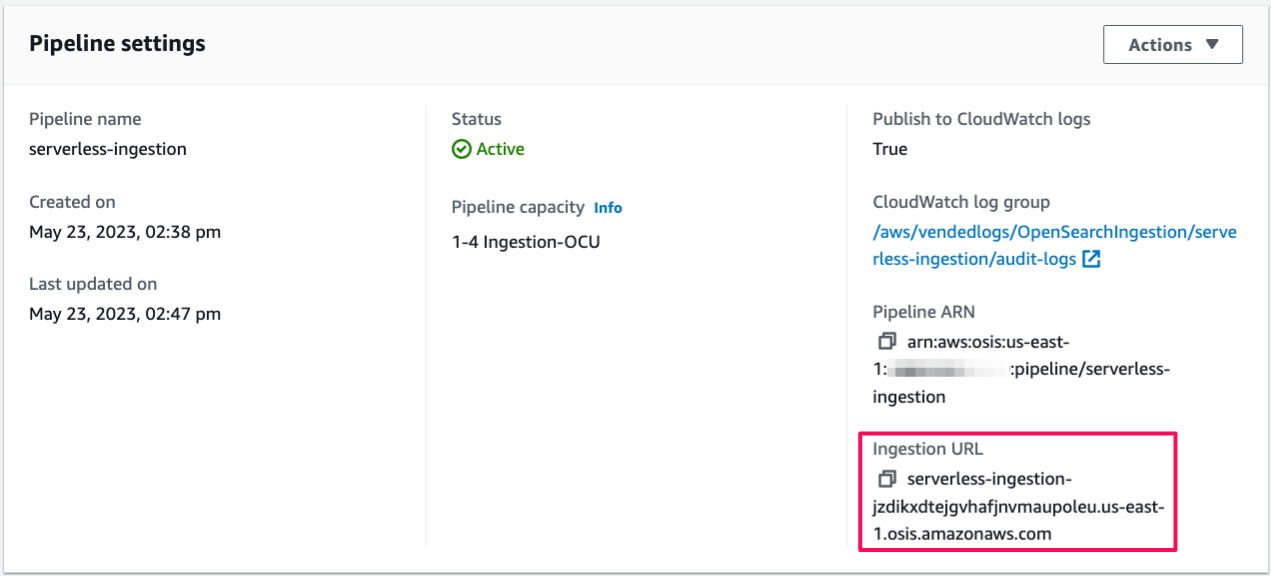
Then, ingest some sample data. The following sample request uses [awscurl](https://github.com/okigan/awscurl) to send a single log file to the `my_logs` index:
$ awscurl --service osis --region us-east-1 \
-X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '[{"time":"2014-08-11T11:40:13+00:00","remote_addr":"122.226.223.69","status":"404","req
uest":"GET http://www.k2proxy.com//hello.html HTTP/1.1","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; WOW64; SLCC2;)"}]' \
https://{pipeline-endpoint}.us-east-1.osis.amazonaws.com/log-pipeline/test_ingestion_path
You should see a `200 OK` response.
#### Step 2: Query the sample data
Now, query the `my_logs` index to ensure that the log entry was successfully ingested:
$ awscurl --service aoss --region us-east-1 \
-X GET \
https://{collection-id}.us-east-1.aoss.amazonaws.com/my_logs/_search | jq -r '.'
**Sample response:**
{
"took": 367,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 0,
"successful": 0,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "my_logs",
"_id": "1%3A0%3ALkidTIgBbiu_ytx_zXnH",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"time": "2014-08-11T11:40:13+00:00",
"remote_addr": "122.226.223.69",
"status": "404",
"request": "GET http://www.k2proxy.com//hello.html HTTP/1.1",
"http_user_agent": "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; WOW64; SLCC2;)",
"@timestamp": "2023-05-24T07:16:29.708Z"
}
}
]
}
}
## References
* [Tutorial: Ingesting data into a collection using Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/osis-serverless-get-started.html)
* [Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion Developer Guide](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/ingestion.html)
* [Data Prepper](https://opensearch.org/docs/latest/data-prepper/index/) - a server-side data collector capable of filtering, enriching, transforming, normalizing, and aggregating data for downstream analytics and visualization.
* [Top strategies for high volume tracing with Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion (2023-04-27)](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/big-data/top-strategies-for-high-volume-tracing-with-amazon-opensearch-ingestion/)
* [Use cases for Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion
](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/use-cases-overview.html) - some common use cases for Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion.
* [Best practices for Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/osis-best-practices.html)
* [Identity and Access Management for Amazon OpenSearch Serverless](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/security-iam-serverless.html#security_iam_id-based-policy-examples-data-plane.html)
* [Setting up roles and users in Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/opensearch-service/latest/developerguide/pipeline-security-overview.html)
* [AWS Signature Version 4 Signing Examples](https://github.com/aws-samples/sigv4a-signing-examples)
* [awscurl](https://github.com/okigan/awscurl) - curl-like tool with AWS Signature Version 4 request signing.