- ### Deep Dive on the Backend
- #### Overview of Architecture
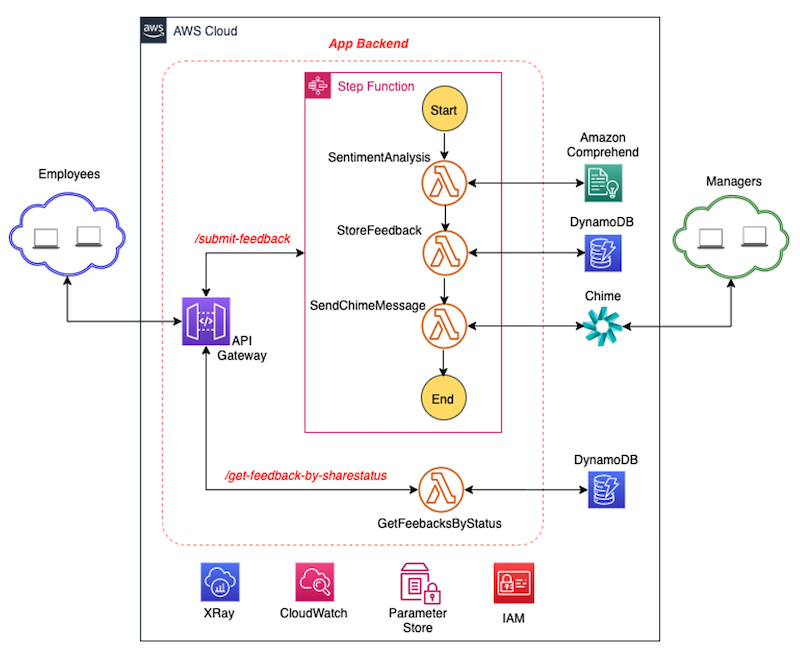
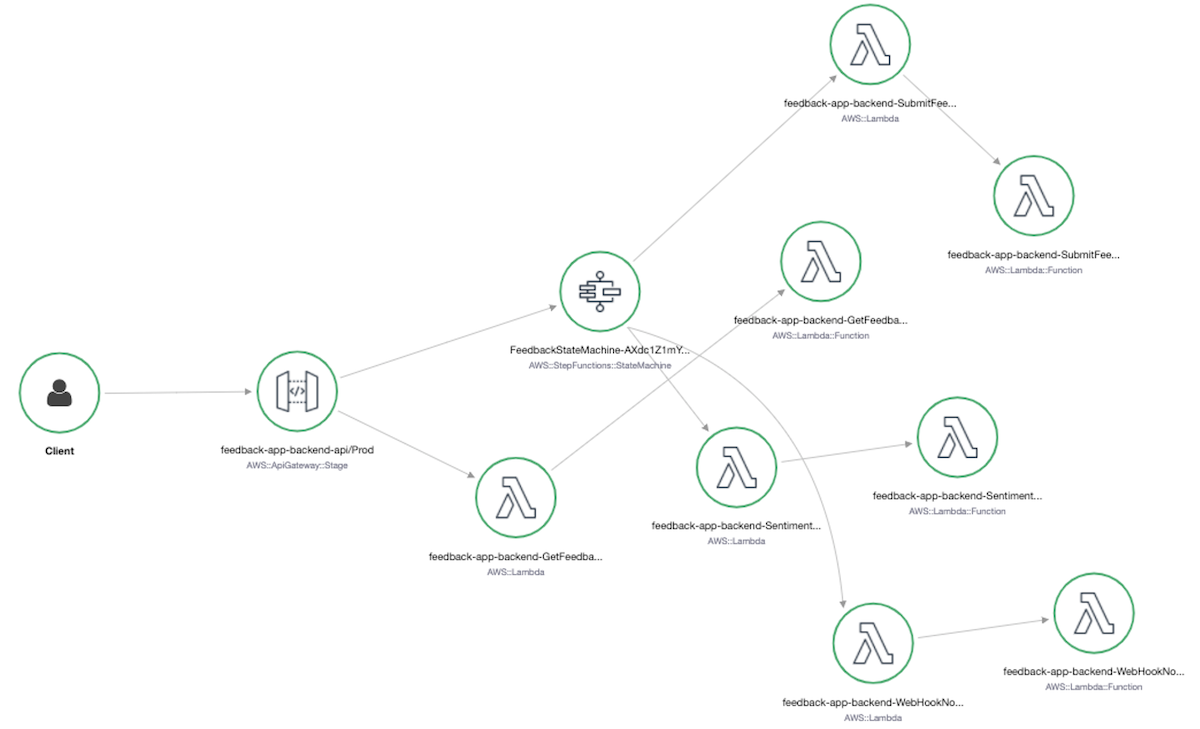
The backend API exposes two resources:
1. /submit-feedback, a POST method for submitting a new feedback
2. /get-feedback-by-sharestatus, a GET method for retreiving feedback based on the whether it is public or private
**`Submit Feedback`**
A feedback submission from the frontend triggers the invokes the /submit-feedback api which triggers an AWS Step Function. The purpose of the step function is to orchestrate the lambda functions created to process a new feedback submission. The 3 lambda function for processing feedback carry out the following:
1. Sentiment Analysis - the feedback comment is analysed usings Amazon Comprehend which returns either "POSITIVE", "NEGATIVE" or "NEUTRAL" depending on the sentimemnts on the feedback. This is achieved using Amazon Comprehend SDK.
2. Persisting Feedback - the feedback details together with the output of the sentiment analysis is stored in DynammoDB using the SDK
3. Notification - the feedback details is formated with markdown and sent to the manager chime room via webhook.
**`Public Feedback`**
The public feedbacks are the feedbacks that the employee have indicated can be shared while submitting the feedback. A Global Secondary Index is created in DynamoDB with the share_feedback attribute set as the partition key. Using DynamoDB SDK, a call is made to the database to retrieve the public feedbacks.
- #### Integration with Chime
Follow the instruction [here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/chime/latest/ug/webhooks.html) to create a webhook for a chime room. The webhook URL is stored in AWS Paramter Store, a default value (which needs to be updated) is specified in the SAM template [here](../feedback-app-backend/template.yaml) within the "WebhookURLSSMParameter" resource. Update the SAM template with the webhook URL and run the commands below to build and deploy the changes.
- **`cd /home/ec2-user/environment/aws-serverless-feedback-app/feedback-app-backend/`**
- **`sam build`**
- **`git add .`**
- **`git commit -m "updated webhook url"`**
- **`git push -u codecommit main`**
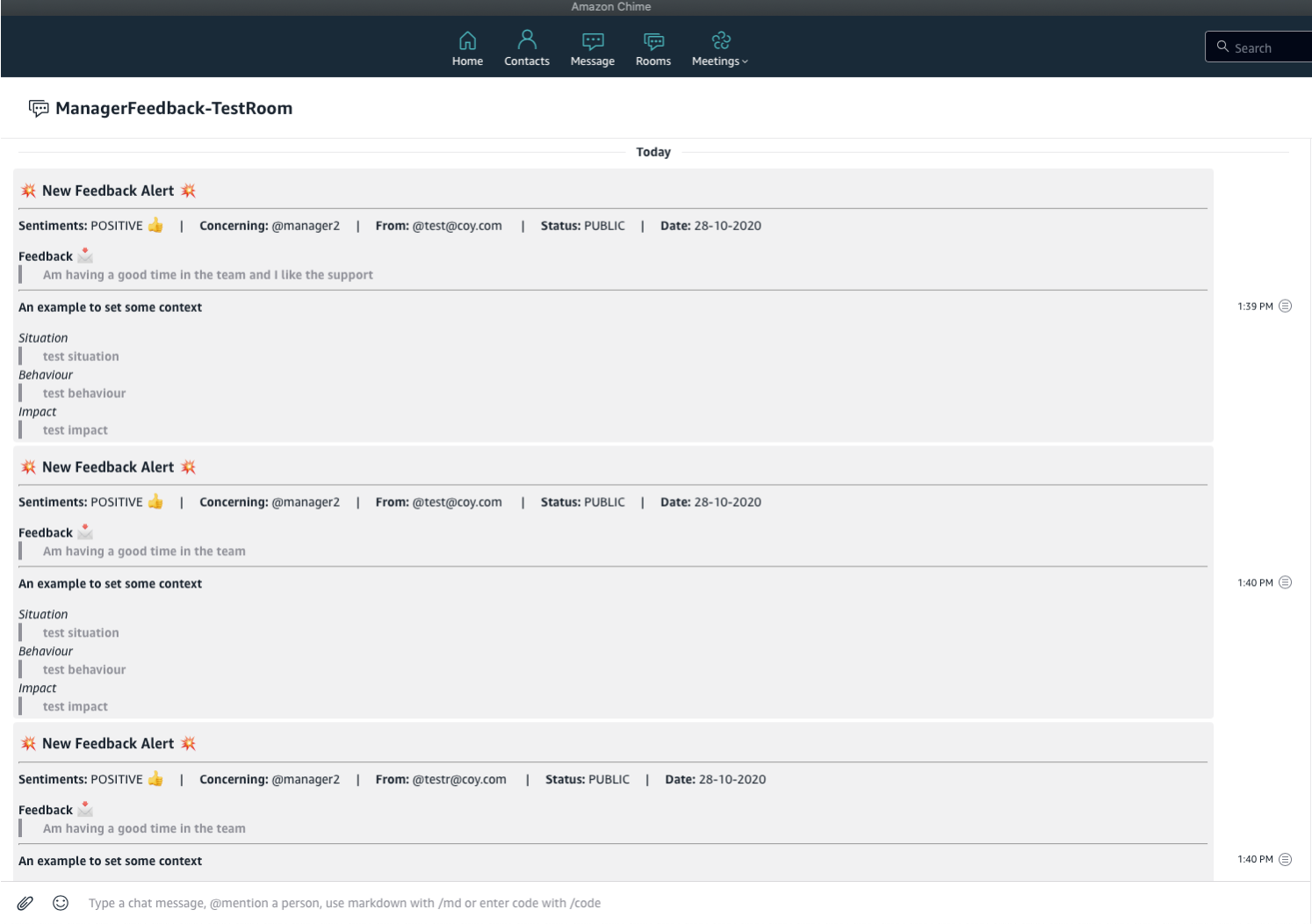
The webhook url is retrieved from parameter store within the lambda function by using the SSM Paramater Store SDK. The template for the markdown formatting to display the notification as shown below can be found [here](../feedback-app-backend/webhooknotification-service/resources/chime_message_template.txt)
- #### Infrastructure as Code
The backend resources which include: API Gateway, Step Machine, Lambda Functions, DynamoDB and Parameter in Parameter Store are created using [AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM)](https://aws.amazon.com/serverless/sam/). AWS SAM extends AWS CloudFormation to provide a simplified syntax for defining the Amazon API Gateway APIs, AWS Lambda functions, and Amazon DynamoDB tables needed by your serverless application. Given this is a simple web application that leverages AWS serverless services, AWS SAM is a good fit that makes it easier to create these resources in yaml and easily deploy the resources to AWS. AWS SAM also provide local testing using SAM local to test the serverless app on a local machine prior to deploying to AWS. The template that defines the configuration of these resources can be found [here](../feedback-app-backend/template.yaml).
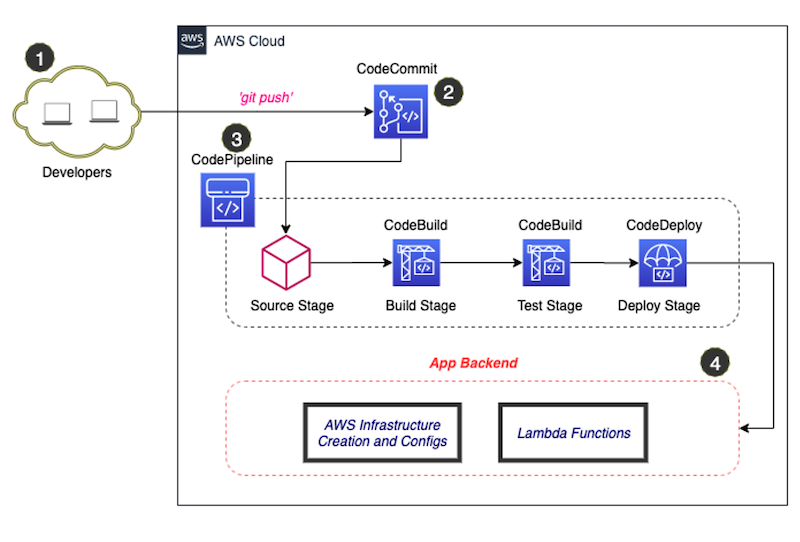
The resources for the CI/CD pipeline which includes AWS CodeCommit, AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild and AWS CodeDeploy were created with [AWS Cloud Development Kit](https://aws.amazon.com/cdk/). Using a familiar programming language like Typescript (as against using yaml), these resources can be created and configured as specified in the file [here](../feedback-app-backend/cicd-pipeline/lib/cicd-pipeline-stack.ts).
- #### CI/CD Pipeline
The CI/CD pipeline is used to automate the build, test and deployment of the infrastructure resources and lambda functions for the backend. The pipeline is triggered by committing code to the CodeCommit repository where the CodePipeline kicks off the building of the sam template as specified [here](../feedback-app-backend/buildspec.yaml) using AWS CodeBuild. AWS CodeDeploy is used to deploy the artifacts as a CloudFormation stack. This deployment will create the AWS resources including the lambda function with source codes.
- #### Logging and Monitoring
Logging and Monitoring is achieved through [AWS CloudWatch](https://aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/) and [AWS X-Ray](https://aws.amazon.com/xray/). One of the benefits of using SAM is that it automatically creates a CloudWatch Dashboard with metrics for of the serveless resource in the SAM template. It also provides insights for each of the lambda function. You can view these metrics and insights by navigating to the SAM application on the AWS console.
Tracing is achieved with AWS X-Ray which is configured by enabling tracing in the SAM template for the API Gateway, [Lambda Functions](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/services-xray.html), [Step Function](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/introducing-aws-x-ray-new-integration-with-aws-step-functions/). X-Ray provides service maps that show information about the API and all of its downstream services as shown below. From the service map, you can zoom in to see a trace view of your API stage. The trace will display in-depth information regarding your API, represented as segments and subsegments.
- #### Cost and Performance Tunning
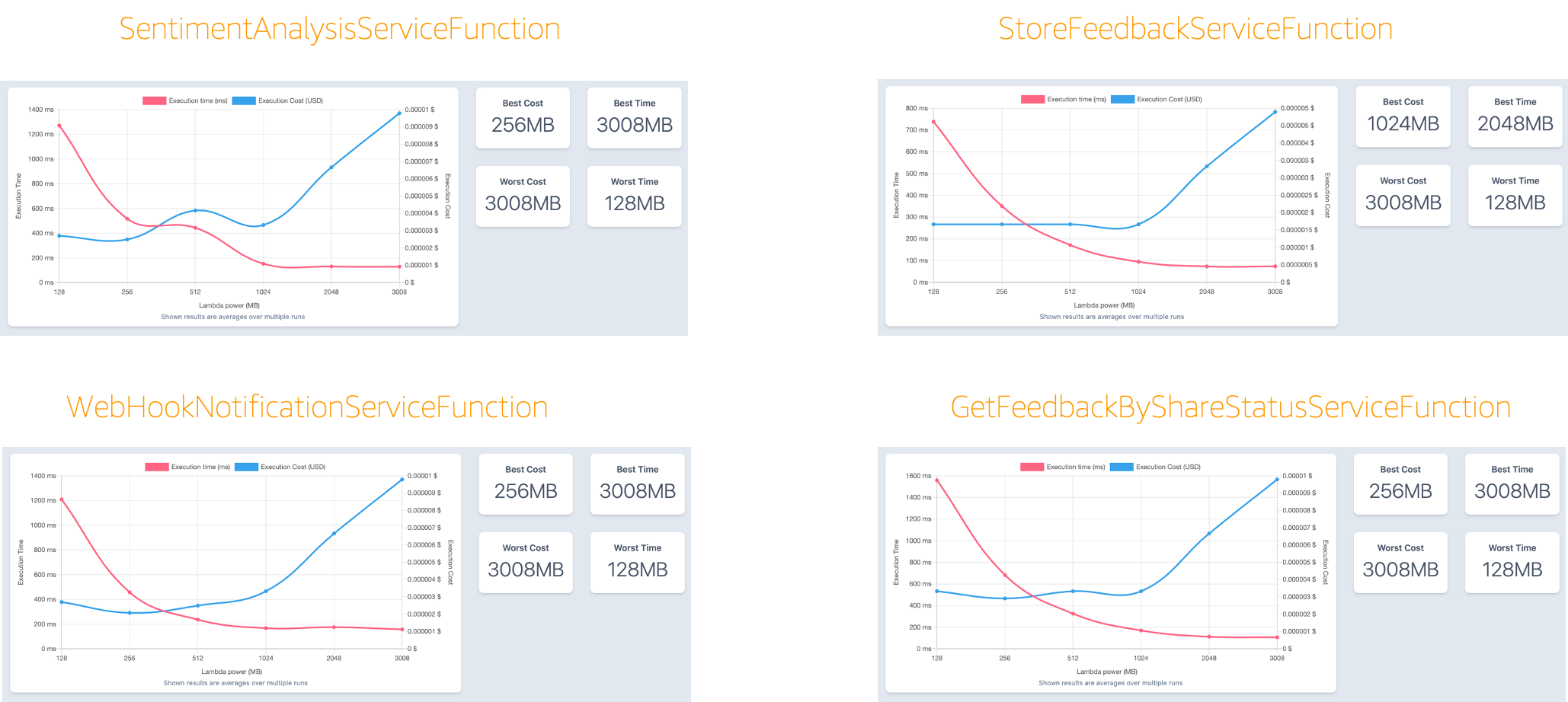
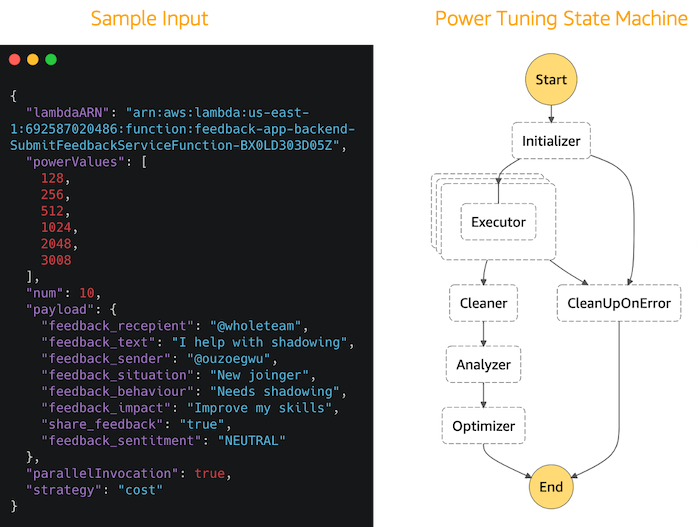
To optimise the lambda functions and ensure that the cost and/or performance targets are met, an open source tool [AWS Lambda Power Tunning](https://serverlessrepo.aws.amazon.com/applications/arn:aws:serverlessrepo:us-east-1:451282441545:applications~aws-lambda-power-tuning) can be deployed to identify the optimal settings for cost and/or performance. AWS Lambda Power Tuning is an AWS Step Functions state machine that helps you optimize your Lambda functions in a data-driven way.The state machine is designed to be quick and language agnostic. You can provide any Lambda function as input and the state machine will run it with multiple power configurations (from 128MB to 3GB), analyze execution logs and suggest you the best configuration to minimize cost or maximize performance.
This tool was used to identify the power configuration to minimize cost for the lambda functions. The first diagram below shows the input to the tool for one of the lambda functions (SubmitFeedbackServiceFunction). The input include:
- ARN of the lambda function
- The lambda memory configuration to test
- The number of invocations for each lambda memory configuration
- The payload to the lambda function
- Whether to initate the lambda functions in parallel
- The strategy to test which in this case is minimum cost
Other parameters can be provided as specified in the [documentation](https://serverlessrepo.aws.amazon.com/applications/arn:aws:serverlessrepo:us-east-1:451282441545:applications~aws-lambda-power-tuning).
The digram below shows the output from running the tool on the four lambda functions used in the application. It can be seen that 256MB is the memory configuration that will give the minimum cost for SentimentAnalysisServiceFunction, WebHookNotificationServiceFunction, GetFeedabackByShareStatusServiceFunction while for StoreFeedbackServiceFunction, 1024MB is the memory configuration that will give the minimum cost. The tools also provide the memory setting that will result in underutilization (worst cost)