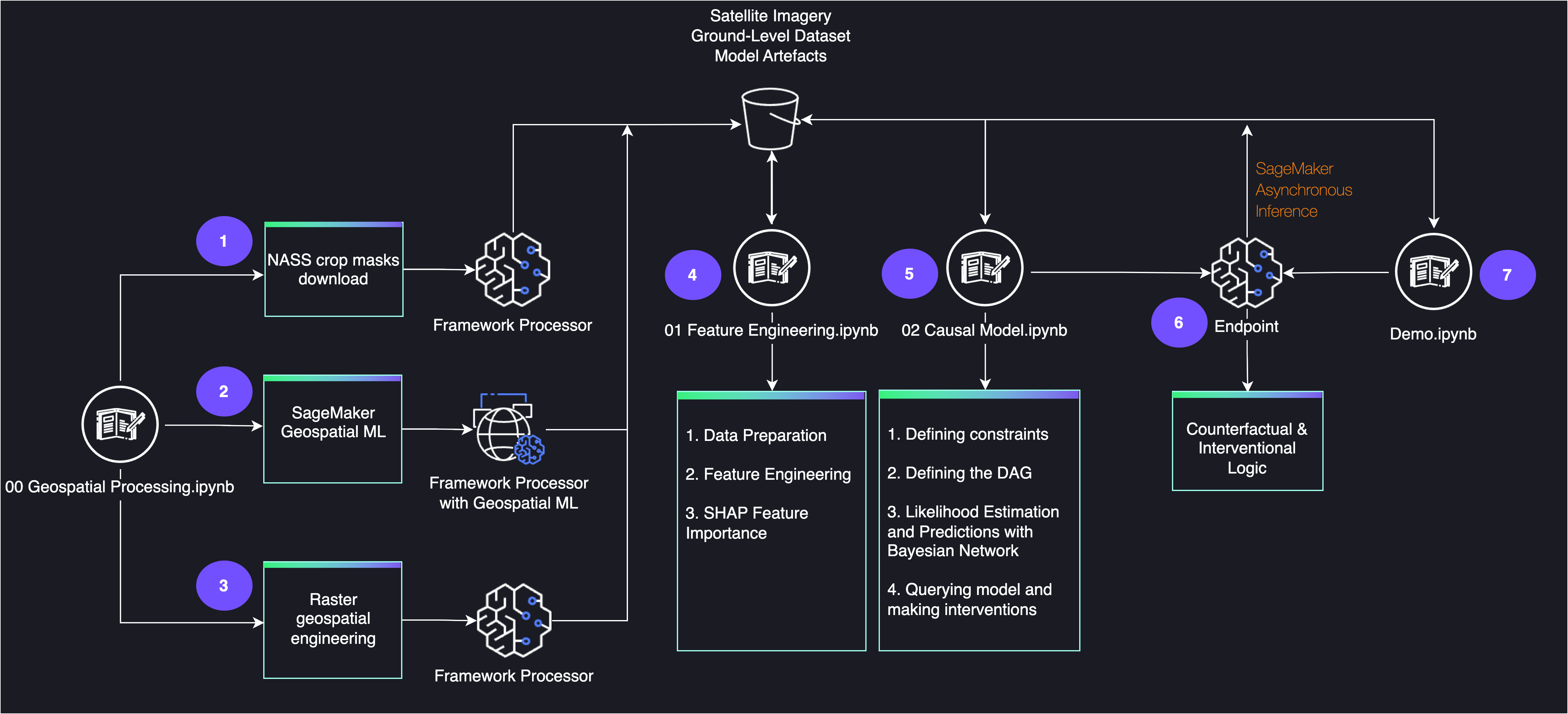

|
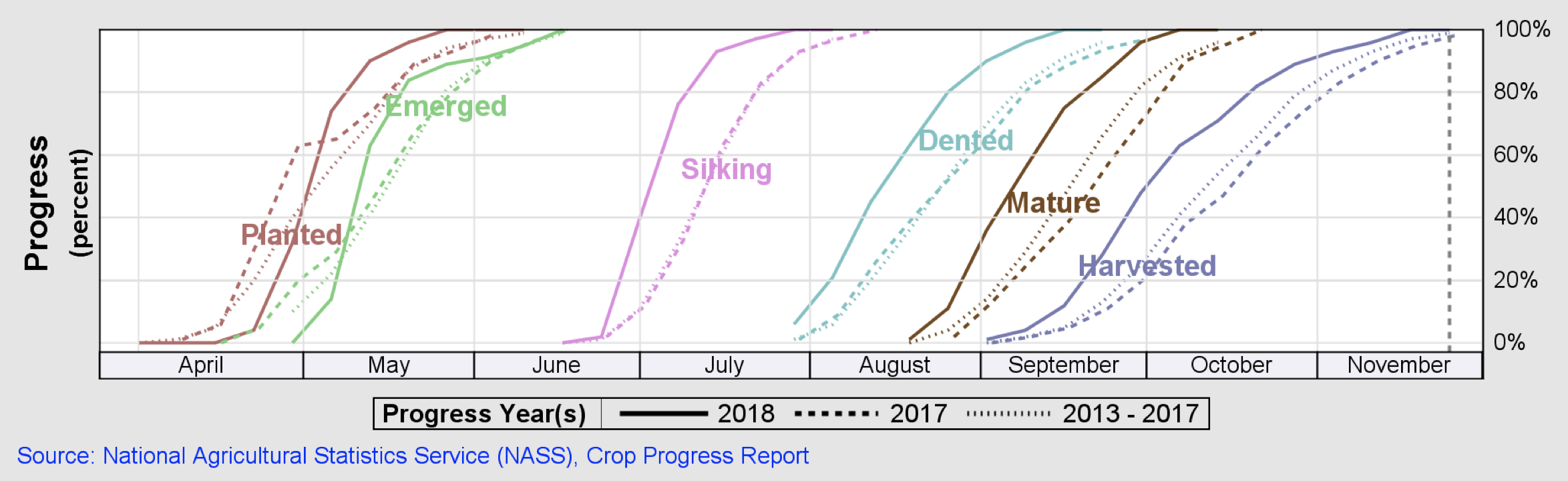
| Vegetative Stages v5 - R1: $\color{green}{\text{emerged}}$ |
| Reproductive Stages R1 - R4: $\color{pink}{\text{silking}}$ |
| Reproductive Stages R5 - R6: $\color{skyblue}{\text{dented}}$, $\color{olive}{\text{mature}}$ |
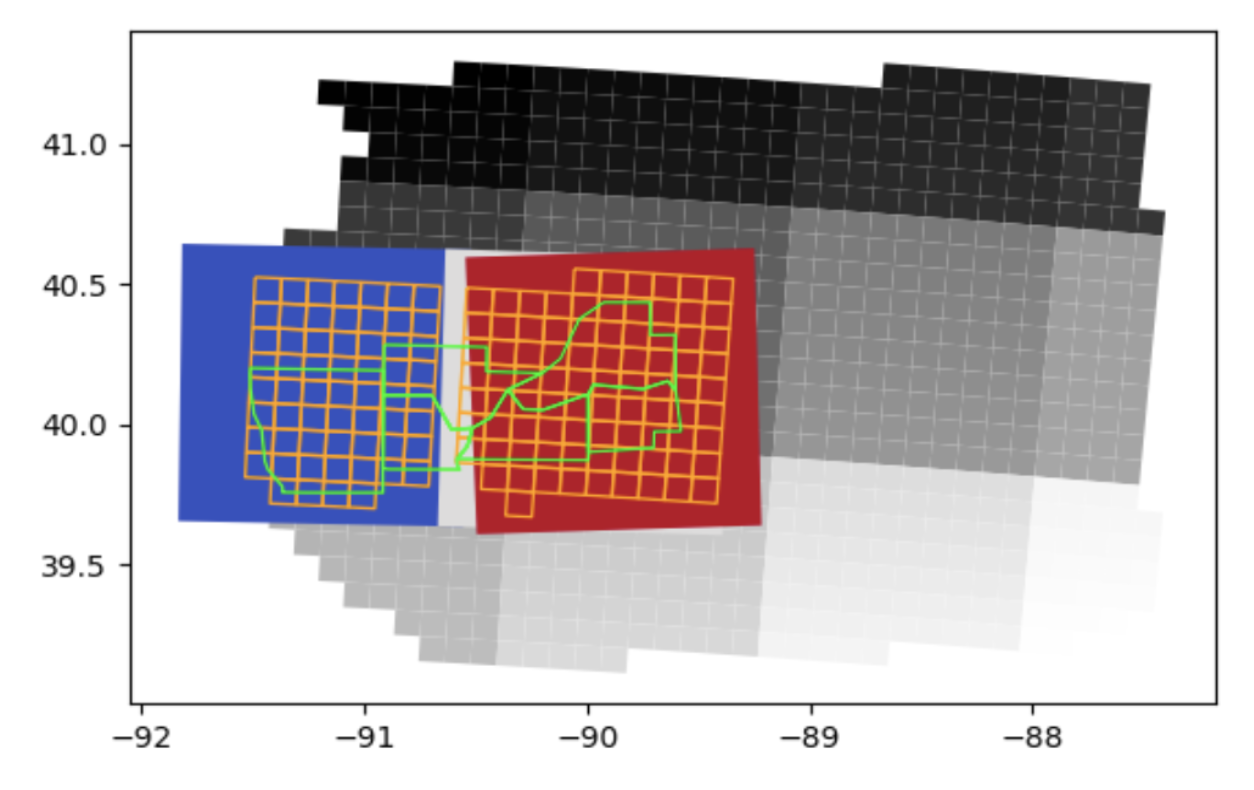
|
| green polygons: counties |
| orange grid: 10 km x 10 km cells |
| large squares grid: 100 km x 100 km Sentinel-2 UTM tiling grid |