# AWS Fargate to AWS SFN
This project contains a sample AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) template for deploying an AWS Fargate service running on an Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) cluster with an Application Load Balancer in-front. The AWS Fargate service makes `startExecution` calls to an AWS Step Functions (SFN) state machine. This template uses a custom image without having to pre-push the image to Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) or another container library. This makes use of the in-built `ecs.ContainerImage.fromAsset` method. The custom image has a base route `/` for health checks, and `/startexecution` route for executing the state machine. Environment variables like the state machine ARN and AWS region are passed to the image to enable it to perform actions on the state machine.
This project also shows how to set up an Step Functions Interface Endpoint to the VPC. A VPC Endpoint policy is created to only allow the Fargate task definition to perform actions through the VPC endpoint.
Learn more about this pattern at Serverless Land Patterns: https://serverlessland.com/patterns/cdk-fargate-sfn.
Important: this application uses various AWS services and there are costs associated with these services after the Free Tier usage - please see the [AWS Pricing page](https://aws.amazon.com/pricing/) for details. You are responsible for any AWS costs incurred. No warranty is implied in this example.
Warning: As of this writing, there are known issues with the images built on Apple's M1 chip, which is based on the ARM architecture. You might encounter the following error log on ECS `standard_init_linux.go:228: exec user process caused: exec format error fargate`. More details can be found at [Stackoverflow 'exec user process caused: exec format error' in AWS Fargate Service](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/67361936/exec-user-process-caused-exec-format-error-in-aws-fargate-service)
## Requirements
- [Create an AWS account](https://portal.aws.amazon.com/gp/aws/developer/registration/index.html) if you do not already have one and log in. The IAM user that you use must have sufficient permissions to make necessary AWS service calls and manage AWS resources.
- [AWS CLI](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/install-cliv2.html) installed and configured
- [Git Installed](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git)
- [AWS CDK](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/cli.html) installed and configured
## Deployment Instructions
1. Create a new directory, navigate to that directory in a terminal and clone the GitHub repository:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/serverless-patterns
```
2. Change directory to the pattern directory:
```bash
cd serverless-patterns/fargate-sfn-cdk/cdk
```
3. Install dependencies:
```bash
npm install
```
4. From the command line, configure AWS CDK:
```bash
cdk bootstrap ACCOUNT-NUMBER/REGION # e.g.
cdk bootstrap 1111111111/us-east-1
cdk bootstrap --profile test 1111111111/us-east-1
```
5. From the command line, use AWS CDK to deploy the AWS resources for the pattern as specified in the `lib/cdk-stack.ts` file:
```bash
cdk deploy
```
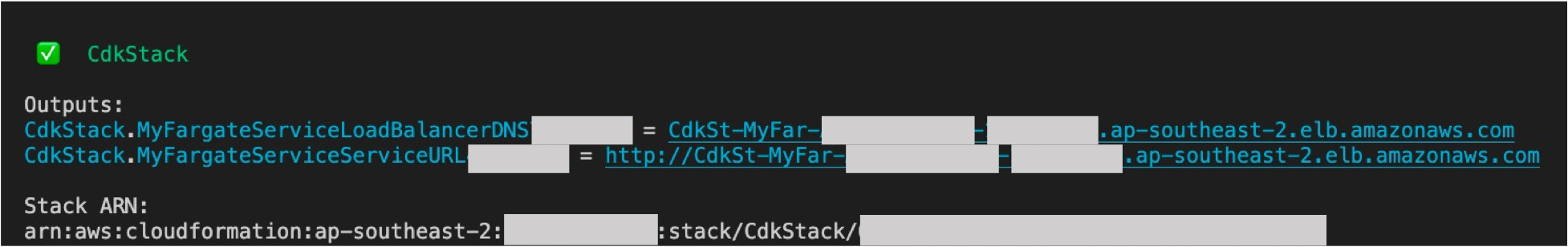
6. Note the outputs from the CDK deployment process. This contains the service endpoint that is used to make POST requests.
## How it works
- The image is constructed directly from sources on disk when `cdk deploy` is executed
- The image is automatically pushed to Amazon ECR
- The State Machine is created
- The ECS cluster is created
- Networking resources are created
- Finally the Fargate Service and the Task Definitions are created. This also passes the environment variables (state machine ARN and region) to the image
## Testing
Retrieve the Fargate Service endpoint from the `cdk deploy` output. Example of the output is:
```
CdkStack.MyFargateServiceServiceURL1234567D = http://CdkSt-MyFar-123456789ABC-123456789.ap-southeast-2.elb.amazonaws.com
```
For reference:
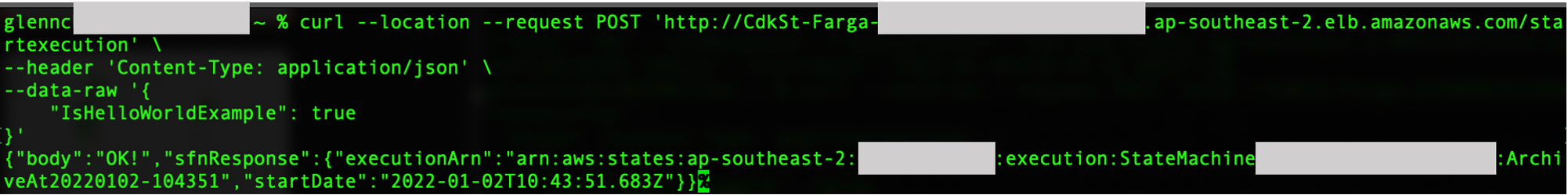
 Make a POST request to the `/startexecution` endpoint. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `true` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": true
}'
# Example
curl --location --request POST 'http://CdkSt-Farga-123456789ABC-123456789.ap-southeast-2.elb.amazonaws.com/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": true
}'
```
Running the request above should produce the following output:
Make a POST request to the `/startexecution` endpoint. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `true` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": true
}'
# Example
curl --location --request POST 'http://CdkSt-Farga-123456789ABC-123456789.ap-southeast-2.elb.amazonaws.com/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": true
}'
```
Running the request above should produce the following output:
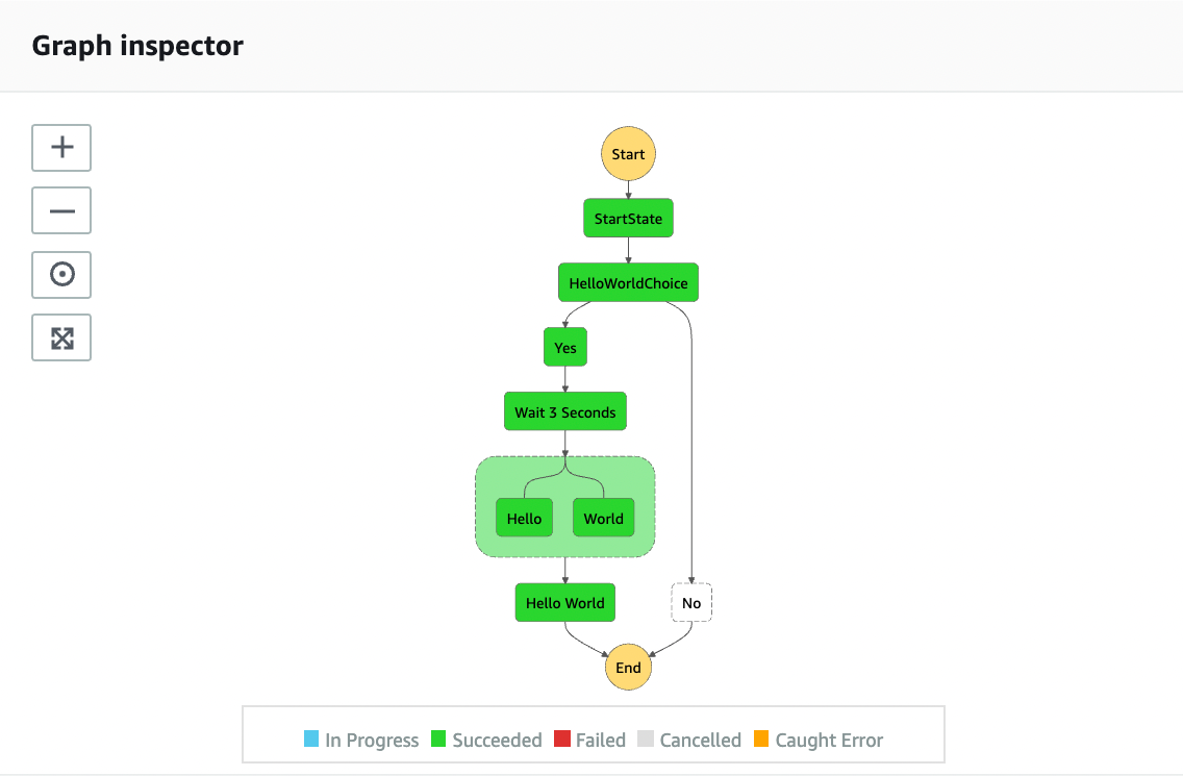
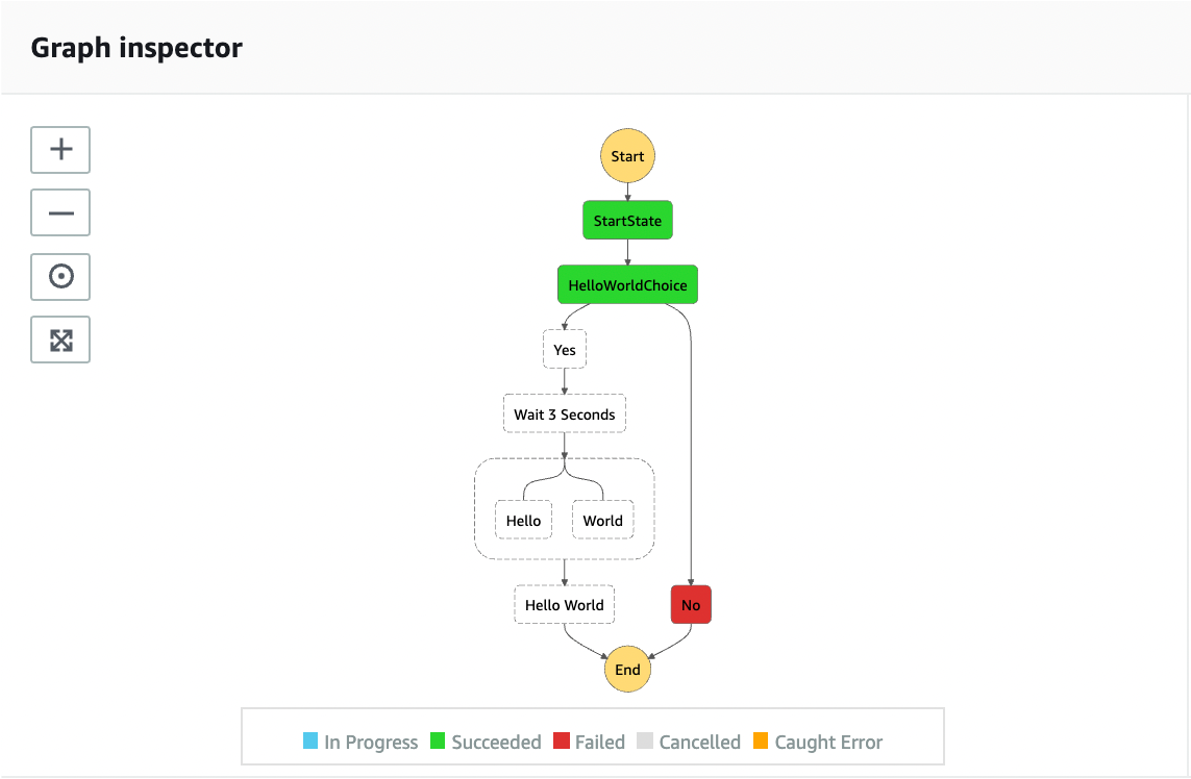
 In the console, the result can be seen as:
In the console, the result can be seen as:
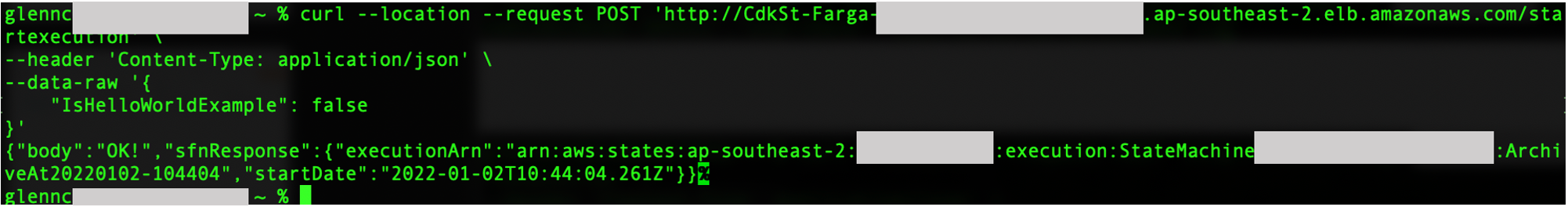
 Alternatively, you can also test by setting the parameter to `false`. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `false` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": false
}'
# Example
curl --location --request POST 'http://CdkSt-Farga-123456789ABC-123456789.ap-southeast-2.elb.amazonaws.com/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": false
}'
```
Running the request above should produce the following output:
Alternatively, you can also test by setting the parameter to `false`. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `false` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": false
}'
# Example
curl --location --request POST 'http://CdkSt-Farga-123456789ABC-123456789.ap-southeast-2.elb.amazonaws.com/startexecution' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"IsHelloWorldExample": false
}'
```
Running the request above should produce the following output:
 In the console, the result can be seen as:
In the console, the result can be seen as:
 ## Cleanup
1. Delete the stack
```bash
cdk destroy
```
2. Navigate to ECR in the AWS console and delete the container images created
---
Copyright 2021 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT-0
## Cleanup
1. Delete the stack
```bash
cdk destroy
```
2. Navigate to ECR in the AWS console and delete the container images created
---
Copyright 2021 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT-0 In the console, the result can be seen as:
In the console, the result can be seen as:
 Alternatively, you can also test by setting the parameter to `false`. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `false` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '
Alternatively, you can also test by setting the parameter to `false`. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `false` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST ' In the console, the result can be seen as:
In the console, the result can be seen as:
 ## Cleanup
1. Delete the stack
```bash
cdk destroy
```
2. Navigate to ECR in the AWS console and delete the container images created
---
Copyright 2021 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT-0
## Cleanup
1. Delete the stack
```bash
cdk destroy
```
2. Navigate to ECR in the AWS console and delete the container images created
---
Copyright 2021 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT-0 Make a POST request to the `/startexecution` endpoint. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `true` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '
Make a POST request to the `/startexecution` endpoint. This executes the State Machine and branches based on the `true` condition. For example:
```bash
curl --location --request POST '