# Flint Index Reference Manual
## Overview
### What is Flint Index?
A Flint index is ...
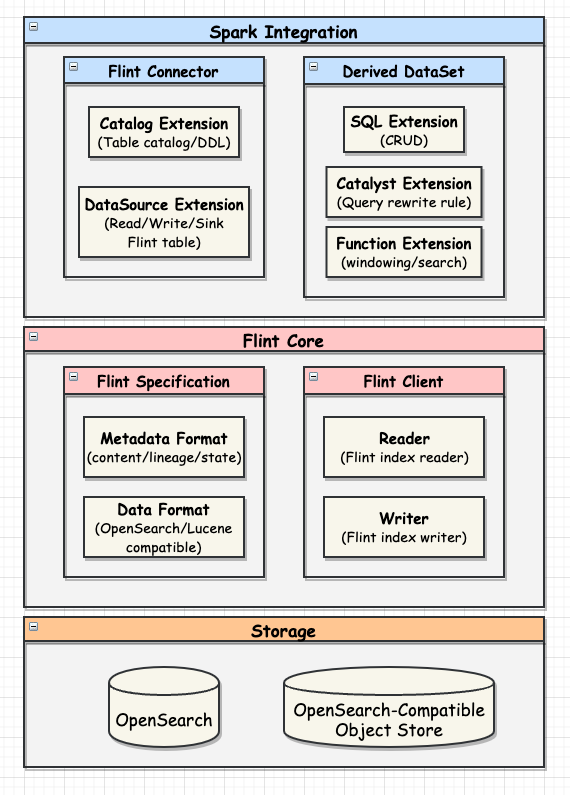
### Feature Highlights
- Skipping Index
- Partition: skip data scan by maintaining and filtering partitioned column value per file.
- MinMax: skip data scan by maintaining lower and upper bound of the indexed column per file.
- ValueSet: skip data scan by building a unique value set of the indexed column per file.
Please see the following example in which Index Building Logic and Query Rewrite Logic column shows the basic idea behind each skipping index implementation.
| Skipping Index | Create Index Statement | Index Building Logic | Query Rewrite Logic |
|----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Partition | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs FOR COLUMNS ( year PARTITION, month PARTITION, day PARTITION, hour PARTITION ) | INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT FIRST(year) AS year, FIRST(month) AS month, FIRST(day) AS day, FIRST(hour) AS hour, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() | SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 ) WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 |
| ValueSet | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs FOR COLUMNS ( elb_status_code VALUE_SET ) | INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT COLLECT_SET(elb_status_code) AS elb_status_code, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() | SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE elb_status_code = 404 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS(elb_status_code, 404) ) WHERE elb_status_code = 404 |
| MinMax | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs FOR COLUMNS ( request_processing_time MIN_MAX ) | INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT MIN(request_processing_time) AS request_processing_time_min, MAX(request_processing_time) AS request_processing_time_max, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() | SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE request_processing_time = 100 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE request_processing_time_min <= 100 AND 100 <= request_processing_time_max ) WHERE request_processing_time = 100
### Flint Index Specification
#### Metadata
Currently, Flint metadata is only static configuration without version control and write-ahead log.
```json
{
"version": "0.1",
"indexConfig": {
"kind": "skipping",
"properties": {
"indexedColumns": [{
"kind": "...",
"columnName": "...",
"columnType": "..."
}]
}
},
"source": "alb_logs",
"state": "active",
"enabled": true
}
```
#### Field Data Type
For now, Flint Index doesn't define its own data type and uses OpenSearch field type instead.
| **FlintDataType** |
|-------------------|
| boolean |
| long |
| integer |
| short |
| byte |
| double |
| float |
| date |
| keyword |
| text |
| object |
#### File Format
Please see Index Store section for more details.
## User Guide
### SDK
`FlintClient` provides low-level Flint index management and data access API.
Index management API example:
```java
// Initialized Flint client for a specific storage
FlintClient flintClient = new FlintOpenSearchClient("localhost", 9200);
FlintMetadata metadata = new FlintMetadata(...)
flintClient.createIndex("alb_logs_skipping_index", metadata)
flintClient.getIndexMetadata("alb_logs_skipping_index")
```
Index data read and write example:
```java
FlintClient flintClient = new FlintOpenSearchClient("localhost", 9200);
// read example
FlintReader reader = flintClient.createReader("indexName", null)\
while(reader.hasNext) {
reader.next()
}
reader.close()
// write example
FlintWriter writer = flintClient.createWriter("indexName")
writer.write("{\"create\":{}}")
writer.write("\n")
writer.write("{\"aInt\":1}")
writer.write("\n")
writer.flush()
writer.close()
```
### API
High level API is dependent on query engine implementation. Please see Query Engine Integration section for details.
### SQL
DDL statement:
```sql
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX
ON